* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Engineering
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
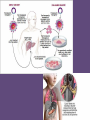
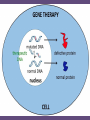
Genetic Engineering : directly manipulating an organism’s DNA using technology Selective Breeding Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans breed other animals and plants for particular traits. Typically, strains that are selectively bred are domesticated, and the breeding is normally done by a professional breeder. • Selective Breeding • Selective breeding of domesticated animals is an example of artificial selection, which occurs when man directly intervenes in the breeding of animals to produce desired traits in offspring • Examples of selective breeding include: • Breeding horses for speed (race horses) versus strength and endurance (draft horses) • Breeding dogs for herding (sheepdogs), hunting (beagles) or racing (greyhounds) • Breeding cattle for increased meat production or milk Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) : an organism whose DNA has been changed using genetic engineering Cloning • The most common cloning method, known as "somatic cell nuclear transfer" or simply "nuclear transfer," requires two kinds of cell. One is a somatic cell, which is collected from the animal that is to be cloned (known as the "genetic donor"). A somatic cell is any cell other than a sperm cell or egg cell, and contains the complete DNA, or genetic blueprint, of the animal it came from. For cloning purposes, somatic cells are typically obtained by a routine skin biopsy performed by a veterinarian. The other kind of cell required for cloning is an egg cell, which is collected from a female of the same species (known as the "egg donor"). In the lab, a scientist extracts and discards the nucleus of the egg cell, which is the part of the cell that contains the egg donor's genes. The scientist then inserts the somatic cell from the genetic donor into the egg and "fuses" the two with electricity. The resulting fused egg contains the genetic donor's DNA. Gene Splicing : “cutting” a gene from one organism to combine it with genes from another organism : forms recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA : DNA that has been spliced together artificially : Genes come from more than one organism DNA Fingerprint : method of mapping a person’s DNA to identify them : used in forensics DNA Fingerprinting • • • • What can we use DNA fingerprinting for? Identification Crime Paternity Gene Therapy : the use of genes to treat or prevent disease Genetically Modified Organisms • http://www.reuters.com/news/picture/geneti cally-modified-animals?articleId=USRTXTZ7A