* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 7.3
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
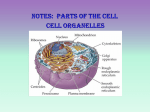
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Cell wall Rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane Provides support and protection Made of cellulose Allows materials to pass through it but not selectively like plasma membrane Nucleus- (the leader) Control center for the cell Directs protein production Contains chromatin Strands of DNA (the blueprint) Forms chromosomes when cell divides Nucleolus Located within nucleus and produces ribosomes Cytoplasm Clear fluid inside the cell Suspends the cell’s organelles Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Site for cellular chemical reaction A workspace Also serves as a transport systems to move things around the cell Ribosomes attach to the ER in areas called rough ER. Here they produce proteins Areas that don’t have ribosomes are called smooth ER Shaped like a stack of pancakes Sort and package proteins to be sent to other parts of the cell Like mail being sorted at a post office Vacuoles Storage vessels for the cell Sack surrounded by a membrane Plant cells have much larger water vacuoles than animal cells Lysosomes Contain digestive enzymes Digest excess or worn out organelles Also digest food particles, bacteria etc. Can fuse with a vacuole and dump its enzymes into it. Chloroplasts Found in plant cells Site of photosynthesis Capture light energy and change it to chemical energy Contain chlorophyll Green pigment that traps energy from the sun Mitochondria The powerhouse of the cell Site of respiration Inner membrane is highly folded Breaking down of food we eat to produce energy In the form of ATP Gives more surface area for more chemical reactions to take place Cells that require more energy have more mitochondria Ie. Muscle cells Cytoskeleton Made of rods and filaments that form a framework for the cell Unlike your bones, it is always changing form Cilia and flagella Structures used for locomotion Hair-like Cilia are usually short, flagella are longer Made of microtubules Thin hollow cylinders made of protein