* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chromosomes
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
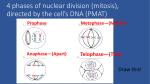
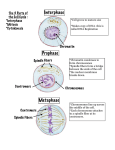
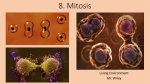
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION Why do cells divide? DNA OVERLOAD 1. _____________________ As cell grows bigger demand on DNA “genetic library” becomes too great Material exchange can’t keep up 2. _____________________ As cell grows bigger demand for transport across membrane is too great Ability to transport of oxygen, food, waste across cell membrane depends on _______________ SURFACE AREA Need for these depends on ___________ CELL VOLUME As cell grows these DON’T increase at the same rate BIGGER CELLS NEED MORE FOOD and OXYGEN, but CAN’T TRANSPORT IT FAST ENOUGH or IN BIG ENOUGH QUANTITIES! http://www.animationlibrary.com Multicellular organisms grow mainly by increasing cell number DNA CAN BE: SPREAD OUT IN NON-DIVIDING CELLS CHROMATIN SCRUNCHED UP IN DIVIDING CELLS CHROMOSOMES DNA in PROKARYOTES • BACTERIAL DNA is CIRCULAR • HAVE ONE CHROMOSOME • NO NUCLEUS DNA in PROKARYOTES • Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules – Help bacteria to survive stress – Antibiotic resistance • Recombinant DNA technology – Insulin: http://www.abpischools.org.uk/page/modules/di abetes/diabetes6.cfm?coSiteNavigation_allTopic =1 DNA in EUKARYOTES • DNA is RODSHAPED CHROMOSOMES • MANY PAIRS • FOUND IN NUCLEUS • DNA in one human cell would be about 6 feet long if it were all stretched out (Karyotype) DNA in EUKARYOTES • Diploid • When a (somatic) cell contains two sets of chromosomes • Humans: 2n=46 • Haploid • When a (gamete) cell contains one set of chromosomes • Humans: n=23 • Zygote • Fertilized egg cell (Karyotype) Chromosome structure • Telomere – A region of repetitive nucleotide sequences – Protects the end of the chromosome from deterioration or from fusion with neighboring chromosomes – Telomerase replaces telomeres – Shortens each time a cell divides – Associated with aging and cancer Chromosome structure • ______________ CHROMATIDS 2 identical arms • _____________ CENTROMERE constricted area holds chromatids together HOMOLOGOUS •__________________ PAIR 2 of each chromosome (one from mom; one from dad) HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES • SAME SIZE • SAME SHAPE • CARRY GENES for the SAME TRAITS IDENTICAL • BUT NOT ______________! (Don’t have to have the SAME CHOICES) http://arnica.csustan.edu/biol3020/cell_division/cell_division.htm CELL DIVISION in PROKARYOTES Bacteria reproduce using BINARY FISSION __________________________________ http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/mitosis/fission.jpg CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE – non-dividing phase G1- Grow bigger Cell is “doing its job” DNA is spread out as chromatin S - Synthesis (copy DNA) & chromosomal proteins G2- Grow bigger, make organelles & molecules needed for cell division CELL DIVISION MITOSIS – Nuclear division Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis – Cytoplasm divides G0 – cell stops dividing (Ex: nerve cell) INTERPHASE (G1 - S - G2) •In between divisions •Cells are in this phase most of the time •Can see nucleus •DNA spread out as chromatin Can’t see chromosomes DNA gets copied (S) Cell gets ready to divide PROPHASE 1st dividing phase •DNA scrunches into chromosomes •Centrioles appear in centrosome region & move to poles •Nuclear membrane & nucleolus disappear •Spindle fibers form & attach to chromosomes CENTROSOME ________ region organizes spindle Spindle MICROTUBULES are part of cytoskeleton METAPHASE Chromosomes line up in middle ___________ ANAPHASE Centromeres split apart Centrioles pull chromatids_______ TELOPHASE (reverse prophase steps) two nuclei See ______ Nuclear membrane & nucleolus return Chromosomes spread out as chromatin Centrioles disappear Spindle fibers disappear CYTOKINESIS Cytoplasm splits into 2 cells ANIMAL CELLS pinch cytoplasm in two with a ______________________ CLEAVAGE FURROW CYTOKINESIS Cytoplasm splits into 2 cells PLANT CELLS can’t pinch because they have a sturdy ____________ CELL WALL Plant cells separate cytoplasm by CELL PLATE growing a _______________ down the middle. Figure 10–5 Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 10-2 Spindle forming Centrioles Nuclear envelope Chromatin Interphase Centromere Chromosomes (paired chromatids) Prophase Cytokinesis Go to Section: Spindle Centriole Telophase Nuclear envelope reforming Centriole Individual chromosomes Anaphase Metaphase Figure 10–5 Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 10-2 Spindle forming Centrioles Nuclear envelope Chromatin Interphase Centromere Chromosomes (paired chromatids) Prophase Cytokinesis Go to Section: Spindle Centriole Telophase Nuclear envelope reforming Centriole Individual chromosomes Anaphase Metaphase Figure 10–5 Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 10-2 Spindle forming Centrioles Nuclear envelope Chromatin Interphase Centromere Chromosomes (paired chromatids) Prophase Cytokinesis Go to Section: Spindle Centriole Telophase Nuclear envelope reforming Centriole Individual chromosomes Anaphase Metaphase Figure 10–5 Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 10-2 Spindle forming Centrioles Nuclear envelope Chromatin Interphase Centromere Chromosomes (paired chromatids) Prophase Cytokinesis Go to Section: Spindle Centriole Telophase Nuclear envelope reforming Centriole Individual chromosomes Anaphase Metaphase Figure 10–5 Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 10-2 Spindle forming Centrioles Nuclear envelope Chromatin Interphase Centromere Chromosomes (paired chromatids) Prophase Cytokinesis Go to Section: Spindle Centriole Telophase Nuclear envelope reforming Centriole Individual chromosomes Anaphase Metaphase Figure 10–5 Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 10-2 Spindle forming Centrioles Nuclear envelope Chromatin Interphase Centromere Chromosomes (paired chromatids) Prophase Cytokinesis Go to Section: Spindle Centriole Telophase Nuclear envelope reforming Centriole Individual chromosomes Anaphase Metaphase Cell Cycle includes G1 phase Interphase M phase (Mitosis) is divided into is divided into S phase G2 phase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Outline Mitosis http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios10 0/lecturesf04am/lect16.htm