* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
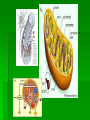
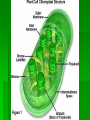
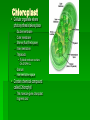
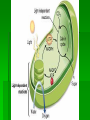
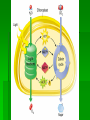
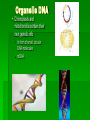
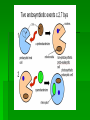
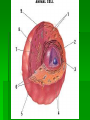
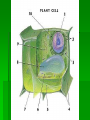
Single-celled organisms and some animals also have vacuoles… Paramecium Contractile vacuole Contracts rhythmically to pump excess water out…this maintains what? homeostasis Cytoskeleton Supporting structure and transportation system Network of protein filaments that helps the cell to maintain its shape and to help the cell move 2 main type of filaments Microtubules Microfilaments (Intermediate filaments is a 3rd type) Microfilaments Threadlike structures Made of protein called ACTIN Extensive networks Tough, flexible framework Help cells move Assembly and disassembly helps cells move (like amoebas) Microtubules Hollow structures Made of proteins called TUBULINS Maintain cell’s shape Important in cell division Make mitotic spindle (separates chromosomes) Help build projections from cell surface… Cilia and Flagella Plural: cilium and flagellum Cilia: hundreds of extension of the cell membrane that move like the oars of a boat Flagella: one or two long extensions off the cell that move in a whip like fashion Enable cells to swim rapidly through liquid Centrioles Only animal cells Made of protein TUBULIN What else is made of tubulin? Near nucleus Help organize cell division Two ways cells get energy… From food molecules From the sun Mitochondria Convert chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use Has 2 membranes Inner membrane Lots of FOLDS (cristae)= INCREASE surface area= more ATP being produced Outer membrane In Animal AND Plant cells Nearly all come from the ovum You get your mitochondria from your mom! Chloroplasts Plant and some Bacteria cells only ( NOT in animal cells) Capture energy from the sunlight and convert it into chemical energy…what is this process called? PHOTOSYNTHESIS Like solar power for plants 2 membranes Inside: large stacks of other membranes that contain chlorophyll Chloroplast (found in cells in leaves) Concentrated in the cells of the mesophyll (inner layer of tissue) in leaf Stomata Tiny pores on surface of leaf Allows carbon dioxide and oxygen in and out of the leaf Veins Carry water and nutrients from roots to leaves Deliver organic molecules produced in leaves to other parts of the plant Chloroplast Cellular organelle where photosynthesis takes place Double membrane Outer membrane Stroma (fluid filled space) Inner membrane Thylakoids Thylakoid membrane contains CHLOROPHYLL Granum Intermembrane space Contain chemical compound called Chlorophyll This molecule gives chloroplast its green color Structure of Chloroplast Structures organize the many reactions that take place in photosynthesis Stomata Small pores in the underside of leaves that release water and oxygen and take in carbon dioxide Guard cells Control the opening and closing of stomata depending on environment Stroma Thick fluid enclosed by the inner membrane Thylakoids Disc-like sacs suspended in the stroma Has membrane that surrounds inner thylakoid space Grana (sing. Granum) Stacks of thylakoids Organelle DNA Chloroplasts and mitochondria contain their own genetic info In form of small, circular DNA molecules mDNA Lynn Margulis American biologist Chloroplasts and mitochondria are descendants of prokaryotes She said… Ancient Prokaryotes from wayyyyy back in the day had a symbiotic relationship with the ancient eukaryotes What is symbiotic? (review ecology!!!) The prokaryotes lived inside the eukaryotes There were prokaryotes that used oxygen to make energy (ATP) Mitochondria There were prokaryotes that used photosynthesis to get energy Chloroplasts Endosymbiotic Theory Idea that mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from prokaryotes Antwon van Leeuwenhook Robert Hook Cell bacteria Cell Theory Electron microscope Prokaryote Eukaryote Organelles Cytoplasm Nuclear envelope Chromatin Nucleus nucleolus Ribosome Smooth ER Rough ER Chromosome Vacuole Osmosis Endocytosis exocytosis Proteins DNA RNA Golgi apparatus Micrometer Millimeter Picameter Lysosome Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Centriole Mictrotubule Microfilament Theodor Schwann Matthias Schleiden Rudolph Virchow Lynn Margulis Endosymbiotic Theory Cilia Flagella Photosynthesis Pseudopodia Aquaporin Transmembrane protein Facilitated diffusion Microscope Micrograph Magnifier Lens Contractile vacuole Central Vacuole Centrioles Centrosomes Nuclear pores Nuclear-plasm Stomata ATP synthase Chlorophyll Cell membrane Cell Wall Cellulose Phospholipids Thylakoid Cristae Matrix Inner membrane Outer memebrane