* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GFP Assays: Live–Cell Translocation Assays
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Green fluorescent protein wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
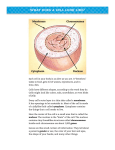
GFP Assays: Live–Cell Translocation Assays • • • • Validated stable cell line: start screening immediately without having to spend months establishing a cell line in-house. Expression vector: offers the flexibility to work with transients and alternative host cell lines Complete right to use: no additional license negotiations are required prior to using the assay Utilizes Aequorea victorea GFP: the established benchmark fluorescent protein technology Live cellular translocation assays employing GFP are becoming increasingly attractive in drug discovery for the development of pharmaceutical screens. Previously intractable targets can be measured by quantitating the real time distribution of GFP-tagged proteins after treatment with test compounds. Exploiting GFP to its full potential requires access to advanced live-cell imaging systems and validated assay technologies. In collaboration with BioImage, Amersham Biosciences has developed a set of translocation assays. These live-cell assays can be used to track protein movements within intra-cellular pathways and highlight any effects caused by potential drug candidates. They also allow you to detect more specific agonists and antagonists and witness that your target protein is active. The results of a translocation assay will give you the clearest picture yet of the effects of your compound on the dynamics within a living cell. The ability to observe the effects on a protein's movement due to your compound (rather than simply measuring changes in its concentration) represents the opportunity to identify a new type of pharmaceutical. Translocation assays therefore represent a new direction for drug discovery. A GFP translocation assay system provides an extensively validated resource for screening and profiling drug effects in living cells. Each assay system comprises of the following: • Fully validated stable cell line (2 vials, 106 cells per vial) • Expression vector containing cDNA for the GFP fusion protein (1 vial, 10ug) • Rights to use; covering patents relating to GFP, the CMV promoter and the fusion protein, if appropriate. • Full technical support manual (including validation data and protocols). These assay systems allow focused real time visualization of your drug's interactions with key signaling pathways without the need for consumable detection reagents. They also provide a view of drug-target interactions with greater speed and precision than measuring gene expression or other downstream events. Ordering information Description GFP-MAPKAP-k2 Assay, non-profit research Code Number 25-9002-60 GFP-Rac1 Assay, Screening 25-9002-61 GFP PLCδ-PH domain Assay Screening 25-9002-62 EGFP-2xFYVE Assay, Screening 25-9002-63 AKT1-EGFP Assay, Screening 25-9002-58 EGFP-STAT3 Assay, Screening 25-9002-64 EGFP-NFAT c1 Assay, Screening 25-9002-65 EGFP-SMAD2 Assay, Screening 25-9002-66 Technical Specifications Assay Signalling Pathways Application areas Translocation MAPKAP-k2 Stress response pathways Nucleus to cytoplasm RAC1 Cytokinesis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis, axon outgrowth, morphogenesis, cell-cell contacts, cell polarity, transformation, adhesion, migration PLCδ-PH domain PI(4,5)P2 signalling pathways, adrenoreceptor function, cytoskeletal organization, responses to purinergic agonists, mechanical stress pathways Growth factor (RTK) and cytokine signalling pathways, PI(3)P levels (class III PI3Kinase sensor) Inflammation, neuronal growth and differentiation, pain, CNS disorders, ischemia, seizures, skeletal muscle regulation Colon and breast cancer, cardiac hypertrophy, myofibrillogenesis, proinflammatory signalling, leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, progression to AIDS Cardiac diseases/ hypertrophy, cardiac injury, Alzheimer’s disease, bipolar disorders Identification of classspecific PI3K inhibitors for development of cancer treatments, immunosuppressants and antiinflammatory drugs Cancer (breast, prostate, ovarian, gastric), tumor progression, drug and radiation resistance in cancer therapy, invasion, angiogenesis, diabetes Acute-phase responses, oncogenesis (hematologic, breast, head, neck, prostate cancers), obesity Immunosuppression, muscle growth Endosomes to cytoplasm Oncogenesis, tumor progression, cardiac hypertension, embryonic development, tissue repair, immune function Cytoplasm to nucleus FYVE AKT1 Cell survival, proliferation, apoptosis, insulin response pathways STAT3 Acute-phase response pathways, cytokine signalling, leptin signalling NFAT c1 Immune responses (IL2, IL4, TNFa gene expression), prostaglandin signalling TGF-beta signalling, growth, differentiation, cell survival, regulation of cell proliferation and migration, elaboration of extracellular matrix SMAD2 Cytoplasm to cell surface ruffles Cell surface to cytoplasm Cytoplasm to cell surface ruffles Cytoplasm to nucleus Cytoplasm to nucleus Algorithm Compatibility Assay Translocation Analysis Module MAPKAP-k2 Nucleus to cytoplasm Nuclear Trafficking RAC1 Cytoplasm to cell surface ruffles Cell surface to cytoplasm Plasma Membrane Spot PLCδ-PH domain FYVE AKT1 Endosomes to cytoplasm Plasma Membrane Trafficking Granularity IN Cell Analyzer 1000 Available IN Cell Analyzer 3000 Available TBD Available Q4 2003 Available Available Available TBD Available Plasma Membrane Spot STAT3 Cytoplasm to cell surface ruffles Cytoplasm to nucleus Nuclear Trafficking Available Available NFAT c1 Cytoplasm to nucleus Nuclear Trafficking Available Available SMAD2 Cytoplasm to nucleus Nuclear Trafficking Available Available G2M CCPM Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Trafficking Q4 2003 Available Cell Cycle: G2M Cell Cycle Phase Marker • • • • Dynamic, non-toxic reporter of cell cycle status in living cells. Enables examination of cell cycle over extended time periods. Higher sample throughput on the IN Cell Analyzer 3000 and IN Cell Analyzer 1000 than flow cytometry. Used in conjunction with the Cell Cycle Trafficking analysis module it is possible to distinguish four stages of the cell cycle: G1/S, G2, prophase and the other stages of mitosis. The assay depends on controlling the expression levels and location of GFP in a cell cycle dependent manner. This is achieved by using functional regions from cell cycle proteins that control reporter expression, destruction and translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. The G2/M cell cycle phase marker assay uses cell cycle specific promoter, destruction and localisation sequences from the key cell cycle modulating protein cyclin B1 fused to GFP. The expression of GFP is restricted to late S and G2 phases by the cyclin B1 promoter. It translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus at prophase due to the cyclin B1 cytoplasmic retention sequence (CRS) and is specifically degraded in metaphase due to the presence of the cyclin B1 D-box . Cell cycle status is therefore determined by interrogating the position and level of GFP in a cell. The assay has been designed for screening of cell cycle perturbing drugs, toxicology testing and lead profiling. Ordering information Description G2M Cell Cycle Phase Marker Assay, Non profit research Code Number 25-9002-55