* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 07.3 Diffusion and Osmosis
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
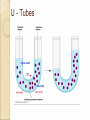
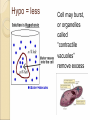
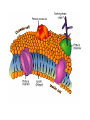
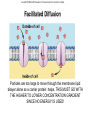
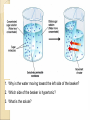
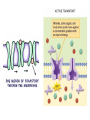
Chapter 7-3 The Cell Membrane; Active & Passive Transport The Cell Membrane •Gatekeeper •Regulates what comes in and out of the cell •Main components: proteins and phospholipids Cell Wall •Found only in plant cells and bacteria cells •Main function is support Solutions •Mixtures of substances •Ex. Salt + water; sugar + water 1. Passive Transport: Diffusion •The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration •Molecules tend to “spread out” •Requires no energy Equilibrium (Cell trying for homeostasis) •When molecules are evenly spread throughout a space Osmosis •The diffusion of water • across a membrane The cell membrane is selectively permeable •Watch the animation Rule for Osmosis If the area outside the cell has more salt – then water will be sucked out of the cell U - Tubes Membrane types: •Permeable- Allows anything to pass in and out •Semi-permeable (selectively)Allows certain things in and out •Non-Permeable- Allows nothing in or out Cells In Different Solutions "ISO" means the same Hypo = less Cell may burst, or organelles called “contractile vacuoles” remove excess water Hyper = more Cell will shrink or die, plants wilt Why is it dangerous to drink sea water? Why does pouring salt on a slug kill it? Passive Transport •Requires no energy •Diffusion & Osmosis •Facilitated Diffusion – carrier proteins “help” molecules across the membrane Particles are too large to move through the membrane lipid bilayer alone so a carrier protein helps, THIS MUST GO WITH THE HIGHER TO LOWER CONCENTRATION GRADIENT SINCE NO ENERGY IS USED! 1. Why is the water moving toward the left side of the beaker? 2. Which side of the beaker is hypertonic? 3. What is the solute? WORD LIST •Diffusion •Osmosis •Selectively permeable •Equilibrium •Solution •Facilitated Diffusion •Hypertonic •Hypotonic •Isotonic •Contractile Vacuole •Passive Transport Know all of these words for the test ACTIVE TRANSPORT •Requires the cell to use energy •Moves things from a lower concentration to higher concentration •Proteins or Pumps found in the membrane move materials across Endocytosis •Taking “in” large molecules by the cell •Phagocytosis = “phood”, taking in food particles •Pinocytosis = liquid substances EXOCYTOSIS • Removing large particles (waste) from the cell • Stuff “exits” the cell • Watch video at http://www.esnips.com/doc/2dad912f-9dcc4936-89d9-1ae32c6125d2/Chapter-6--Endocytosis-and-Exocytosis • Or McGraw Hill Site Add to Word List •Active Transport •Endocytosis •Phagocytosis •Pinocytosis •Exocytosis •Protein Pump