* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function - KEY Structure In Eukaryotes
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
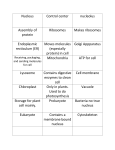
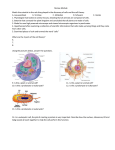
Cell Structure and Function - KEY Structure 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cell Wall 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Envelope In In Plant Eukaryotes, Cells, Animal Prokaryotes, Cells, or or Both? Both? Both Both Eukaryote Eukaryote Both Plant Description Function C. Made of protein and phospholipids. (outer cell layer) D. Selectively permeable (controls material movement into/out of cell) D. Large empty spaces between cellulose fibers (outer cell layer) E. Protects and supports B. Contains the DNA in chromosomes A. Controls the normal activities of the cell Outer boundary of nucleus, consists of double membrane containing pores Controls what enters and leaves the nucleus Both Both Round structure located Makes ribosomes that in nucleus (1 to 3). make proteins 5. Nucleolus Eukaryote Both Drawing Cell Structure and Function - KEY 6. Cytoplasm 7. Ribosomes 8. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 9. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 10. Golgi Bodies Both Both Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Both Both Both Both Both Jelly-like substance enclosed by cell membrane A. Provides a medium for chemical reactions to take place A. Tiny particles floating D. Where protein freely in cytoplasm or synthesis occurs attached to ER 1. Folded system containing a network of hollow membrane tubules 2. lacks ribosomes on its surface 1. Folded system containing a network of hollow membrane tubules 1. Has ribosomes on its surface. 1. Stacks of flattened sacs 3. Makes proteins USED in the cell, also involved in carbohydrate and lipid synthesis 2. Makes membrane proteins and proteins for EXPORT out of cell 4. Transport vesicles with modified proteins pinch off the ends Cell Structure and Function - KEY 11. Lysosomes 12. Vacuole 13. Mitochondria 14. Plastids 15. Chloroplast Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Both Both Both 1. Contain digestive enzymes Spherical shape. 4. Lyse (break open) & release enzymes to break down & recycle cell parts, food & bacteria. Spherical shape. B. Plants have a large central vacuole. C. Animals have a small or absent vacuole. A. Temporary storage (sugars, proteins, minerals, wastes & pigments). Surrounded by a DOUBLE membrane B. Has its own DNA Rod-shaped. B. Generate cellular energy (ATP) from sugar (cellular respiration). A. A plant organelle B. Contain pigments Food storage (i.e. store starch). Rod-shaped. Contain the green pigment chlorophyll. B. Traps in sunlight to make sugar (food). C. Process is called photosynthesis. Plant Plant Cell Structure and Function - KEY 16. Cytoskeleton 17. Peroxisomes 18. Centrioles 19. Cilia 20. Flagella Both Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Both B. Made of proteins. C. Network of fibers constructed of: i. microtubules ii. microfilaments A. Helps cell maintain cell shape. Spherical shaped. Sacs. Use oxygen to break down fats. Pair structure. Small set of microtubules. Help cell divide. Like many little hairs. Example: Lining of windpipe. 1. Movement in unicellular organisms. 2. Use cilia to move fluid over the surface. Generally longer than cilia and limited to one or a few per cell. Example: Sperm 1. Movement in unicellular organisms. Animal Animal Animal Animal