* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Cells / Microscopes
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
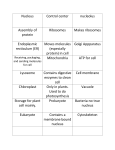
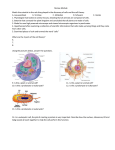
Cell Theory & Eukaryotic Structures • Cellular timeline – 1665… Robert Hooke views cork under a microscope and describes tiny chambers he calls cells – 1674… Anton van Leeuwehoek observes single celled organisms in pond water using a microscope – 1838… Matthias Schleiden states that all plants are made of cells – 1839… Theodor Schwann states that all animals are made of cells – 1855… Rudolph Virchow… establishes the cell theory • Cell theory – All living things are made of cells – Cells are the basic unit of life – New cells come from existing cells • Study called cytology – Light microscopy - a device using light and mirrors to magnify an object. Its resolution (measure of clarity) is limited to 0.2 mm. • good for seeing the gross structure of most cells and bacteria • most appropriate for viewing live specimens – Electron Microscopy - a device that concentrates a beam of electrons onto a plated surface. Its resolution is to around 2nm. (good for seeing organelles and some macromolecules) • (SEM) scanning electron microscope good for detailed investigation of surface structure • (TEM) transmission electron microscope - good for seeing internal structures of cells – Cell fractionation • uses a centrifuge to separate the parts of the cell by mass Exploring the Cell • Prokaryotes - no true nucleus – DNA is not separated from the rest of the cell (no nuclear membrane) but is concentrated in a nucleoid region • Eukaryote - true nucleus – DNA is located in a membrane bound compartment called the nucleus • The nucleus houses the genetic information of the cells. It is responsible for directing protein synthesis which effects every function of the cell. – area between the nucleus and the plasma membrane is called the cytoplasm • contains the membrane bound organelles Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Prokaryote vs Eukaryote • Common features – plasma membrane - all cells are bound by a plasma membrane • functions as a selective barrier - hydrophobic interior with hydrophilic exterior which is embedded with channel proteins used to transport materials. • has a very large surface to volume ration in order to efficiently transfer gases, nutrients, & waste in and out of the cell Prokaryote vs Eukaryote • Prokaryote (Bacteria) – The cell performs everything required for survival • • • • Growth Reproduction Response to environment Movement • Eukaryote (Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals) – Larger and more complex than prakaryotes – Single celled (protists) or multicelled • Cells may highly specialized to carry out specific functions