* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division - Valhalla High School
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
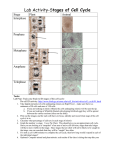
CELL DIVISION Mitosis WHAT IS MITOSIS? Part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides. Results in the formation of 2 identical daughter cells. Mitosis is completed in 4 distinct steps. THE CELL CYCLE Mitosis takes up very little of the life time of a cell. 90% of the time our cells are in between cell divisions. We call this in between time INTERPHASE. INTERPHASE There are 3 phases of interphase in which the cell is carrying out different functions. • G1: First phase of interphase in which a cell does most of its growing. They increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles. • S: The second phase of interphase. Chromosomes are replicated and the synthesis of DNA molecules takes place. • G2: Third phase of interphase. The cell prepares itself for mitosis. PHASES OF MITOSIS Biologists divide the events of mitosis into four phases: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. IPMAT. IPMAT? An easy device to help remember the steps of the cell cycle in the correct order. Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase. PROPHASE First and longest stage of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions of the opposite sides of the nucleus. PROPHASE (CONT.) The nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear during prophase. The spindle fibers begin to form and attach themselves to the centromeres of the chromosomes METAPHASE Second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. ANAPHASE Third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles. TELOPHASE Fourth and final phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes begin to unravel back into chromatin. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus reform. CYTOKINESIS Cytokinesis, while technically not a part of mitosis, results in the physical splitting of the cytoplasm. The sides of the cell membrance pinch inwards creating a cleavage furrow. Afterwards, the two new daughter cells will enter the G1 phase of interphase. PUTTING IT TOGETHER Mitosis in action