* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Summary Peroxisome is a structure present in the all eukaryotic
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
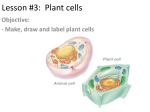
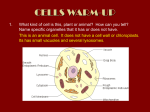
Summary Peroxisome is a structure present in the all eukaryotic cells and are about the size of lysosomes (0.5-1.5 µm). peroxisomes are present near the liver and kidney in animals and in plants they assist photosynthesis. Peroxisomes helps in removing of the H2O2 from the cell by the the enzymes present in them. Any disorder in the peroxisome swill lead to some disorders like Xlinked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) and Zellweger syndrome. A small, spherical, membrane-bound organelle containing a fluid with dissolved molecules. In plant cells, the vacuole takes up a large amount of space, at times, it occupies more than 90% of the plant cell space. It is said that vacuoles are usually formed by the fusion of many membrane vesicles. Due to this reason, a vacuole does not have any specific size or shape. However, when it comes to the vacuole structure, it is designed so as to complement its function. Many mature and grown plant cells usually have a single large vacuole. This vacuole is surrounded by a structure known as a tonoplast. The vacuole contains a fluid known as cell sap. This fluid or cell sap contains different compounds, some of which are secretory and some are excretory in nature. Also the vacuole contains various concentrations of salts, sugars and different kinds of soluble pigments. The cell sap also contains various enzymes that are even capable of digesting the cell itself. Although most mature plant cells contain a large single vacuole. This eventually pushes the cytoplasm, nucleus and other such structures against membrane and the cell wall. the plasma