* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chpt 6 - San Diego Unified School District
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
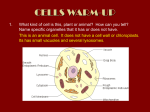
Chpt 6 Outline I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote B. Eukaryote 1. cytoplasm (also in prokaryotes) 2. Plasma membrane (also in prokaryotes) II. Eukaryotic Organelles: A. Nucleus 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Nucleolus 3. Chromosomes B. Ribosome C. Endomembrane system 1. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) a. Smooth ER b. Rough ER 2. Golgi apparatus 3. Lysosome 4. Vacuoles a. food vacuole b. contractile vacuole c. central vacuole (plants) D. Mitochondrion E. Chloroplast (plants) III. Cytoskeleton A. Cilia B. Flagella IV. Extracellular components A. Cell wall (plants) Study Tips: Know … the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. the structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. the structure and function of organelles found only in plant cells or only in animal cells. As an example, be prepared to discuss structures found in plant cells, but not in animal cells. (Plant cells have a large central vacuole, chloroplasts, and a cell wall.)