* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heredity, Environment, and Evolution
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Irving Gottesman wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
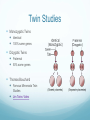
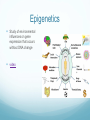
Heredity, Environment, and Evolution Mod 14 and 15 Influences Nature vs Nurture Intelligence Aggression Personality Behavioral genetics Integrates the influences of heredity, environment and evolution in terms of their effect on human behavior Heredity How the traits of parents are transmitted biologically to their offspring Chromosomes Nucleus of each human cell contains 46 chromos 23 from each parent Genes Biochemical units of heredity that make up chromosomes Contain DNA (chainlike molecule) Environment Nature vs Nurture debate Nature – genetic or biological Sets the possibilities for behavior Nurture – environmental factors Determines how the possibilities will be realized Most agree both contribute to influence behavior Evolution Darwin gradual change in genes over time because traits that allowed our ancestors to survive where passed on Twin Studies Heritability Proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes Varies depending on pop. And envir. being studied It is an estimate Applies only to the population as a whole Not to individuals Numerical value 0 to 1 Heritability Trait with high levels of heritability is height If a given population has good health and nutrition, most differences regarding height will be due to differences in their genes video Twin Studies Monozygotic Twins Identical 100% same genes Dizygotic Twins Fraternal 50% same genes Thomas Bouchard Famous Minnesota Twin Studies Jim Twins Video Adoption Studies Genetic relatives Environmental relatives Environment shared by a family’s children has virtually no impact on personality Epigenetics Study of environmental influences on gene expression that occurs without DNA change video Evolutionary Psychology Video overview