* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
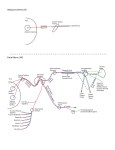
Nervous System I. The Nervous System is a control system in the body A. Parts of the Nervous System i. The Brain ii. The Spinal Cord iii. The Nerves B. How it works i. Carries messages to and from all parts of the body ii. Messages travel along nerve cells (Called Neurons) 1. Nerve Cells (Neurons) are cells that send and receive messages iii. Nerve Cells (Neurons) are found in bundles called Nerves iv. Works similar to an electrical wiring system C. The Brain i. The main organ of the Nervous System ii. Control Center of the body iii. Most messages enter and leave the brain iv. Made of three parts v. Cerebrum 1. Largest part of the brain 2. Folded like a piece of paper to allow more nerve cells to fit inside the skull 3. Divided into right and left halves 4. Halves control opposite sides of the body 5. Controls thinking processes 6. Controls movement of many muscles 7. Different regions control different activities vi. Cerebellum 1. Found just under the back part of the cerebrum 2. Also has many deep folds 3. Helps the muscles work together II. 4. Helps the body keep balance vii. Brainstem 1. Found at the base of the brain 2. Controls the functions that keep you alive 3. Controls all of these actions automatically D. The Spinal Cord i. The Spinal Cord is a thick cord of nerves found in the middle of the back ii. Carries messages to and from the brain iii. Runs through a hole in the backbone iv. All nerves in body branch off of the spinal cord Actions of the Nervous System A. Three types of control i. Voluntary – You choose the action ii. Involuntary – Actions controlled without having to think about them iii. Reflex – Automatic responses without thought controlling the action B. Three types of nerve cells i. Sensory Nerve Cells 1. Carry messages to the spinal cord and the brain 2. Some pick up messages from within the body 3. Others pick up message from outside your body 4. Cells that pick up outside messages are linked to the five senses ii. Motor Nerve Cells 1. Carry messages away from the brain 2. Carry messages to make the muscles move iii. Connecting Nerve Cells 1. Connect sensory nerve cells to motor nerve cells 2. Found within the brain and spinal cord C. Typical Nervous System Response (with example) i. Sensory Nerve Cells pick up an outside message (Telephone rings and is heard by the ear’s sensory nerve cells) ii. Sensory Nerve Cells carry the message to connecting nerve cells in the brain (Brain realizes that the phone is ringing and decides to send the boy to answer the phone) iii. Connecting Nerve Cells in the brain send messages to the Motor Nerve Cells to go answer the phone iv. Motor Nerve Cells tell muscles to get out of chair, walk to phone, pick it up, and talk D. Other Nervous System Response i. Sometimes the Connecting Nerve Cells in the brain are skipped ii. If someone hits your knee, your may get a knee jerk response iii. The Sensory Nerve Cells send a message to the connecting nerve cells in the spinal cord and the spinals cord sends a message to the Motor Nerve Cells to kick iv. This is called a reflex action Endocrine System III. Endocrine System IV. A. Is a group of specialized organs and body tissues that produce, store, and secrete chemical substances known as hormones. B. Hormones are the body’s chemical messengers C. Regulates body’s growth and development D. Controls functions of various tissues E. Supports pregnancy and other reproductive functions F. Regulates metabolism G. Hormones are released directly into the bloodstream Components of the Endocrine system A. Hypothalamus B. Pituitary Gland C. Thyroid D. Parathyroid E. Adrenal Gland F. Pineal Body G. Ovary H. Testis I. Pancreas V. Hypothalamus A. Located deep in the brain B. Controls the pituitary gland C. Coordinates the endocrine system D. Bridges the gap between the nervous system and the endocrine system VI. Pituitary Gland A. Located in a bony cavity just below the base of the brain B. Body’s master gland C. Secretes several hormones that regulate the function of other endocrine glands D. Regulates the body’s growth E. Stimulates milk production in women who are breast feeding F. Also secretes endorphins which are chemicals that act on the nervous system to reduce pain VII. Thyroid Gland A. Located in the neck B. Regulates growth and metabolism C. Plays a crucial role in brain development in children VIII. Parathyroid glands A. Four small glands located at the four corners of the thyroid gland B. Regulates the level of calcium in the blood IX. Adrenal Glands A. Located on top of the kidneys B. Regulate salt and water balance in the body C. Prepares the body for stress D. Regulate metabolism E. Interacts with the immune system F. Produces adrenaline i. Increases blood pressure during stress ii. Increases heart rate during stress iii. Produces the fight or flight response X. Gonads A. Secrete sex hormones B. Reproductive component of the endocrine system C. Female gonads are called the ovaries i. Located in the pelvis ii. Produce female sex hormones iii. Estrogen iv. Progesterone v. Controls development of sexual organs vi. Stimulate the appearance of secondary sex characteristics vii. Regulate menstruation and pregnancy A. Male gonads are called the testes i. Located in the scrotum ii. Produce male sex hormones and sperm iii. Testosterone iv. Controls development of sexual organs v. Stimulate male secondary sex characteristics vi. Stimulate muscle growth XI. Pancreas A. Located in the upper abdomen just under the stomach B. Secretes digestive enzymes into the digestive system C. Produces insulin D. Regulates energy and metabolism XII. Pineal Body A. Located in the middle of the brain B. Regulates the wake/sleep cycle XIII. How the endocrine system works A. Hormones are secreted directly into the blood stream B. Receptors in the target area bind with the hormones and produce chemical changes in response to the body’s needs