* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3-3 Cell Organelles
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
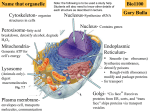
3-3 Cell Organelles Name _______________________ Blanks Notes Period _____ Date ___________ The Nucleus Directs Cell Activities and Stores DNA Most functions of a eukaryotic cell are controlled by the cell’s _____________ which is surrounded by a double _____________ called the _____________ ______________. This is made of two __________ bilayers that separate the ____________ from the _____________. Scattered on the surface are many small channels called _____________ _________, Substances made in the nucleus, such as ribosomal proteins and _______, move through these into the ______________. Ribosomes are partially assembled in the ______________. The _______________ information of a eukaryotic cell is coded in the cell’s _______, which is stored in the _____________. DNA usually exists as long, ________ __________, but when it is about to divide, the DNA strands ________ ____ and look like dense, __________________ structures called _______________. An Internal Membrane System Processes Proteins Eukaryotic cells have a system of internal _______________ that play a role in processing of _____________, which are made on ______________. Each ribosome is made of different ______________ and ______. Some ribosomes are suspended in the _______________ and are called ”______” and these make proteins that remain __________ the ________. These are like the ribosomes in _________________ cells. Production of Proteins – Proteins that are ____________ from the cell, like _____________ molecules, are made by ribosomes on the surface of the _______________ ______________. The ER is an extensive system of internal _______________ that move proteins and other things through the _______. The part of the ER with ____________ ____________ is called the ___________ ER because of its appearance. The rough ER helps ______________ proteins that are made by its _______________ ______________. As the protein is made it crosses the ER _____________ and enters the _____ where a portion of the ER is pinched off to form a ______________. A vesicle is a small, ______________-___________ sac that _______________ substances in cells. Enclosing certain proteins inside vesicles, the cell keeps the proteins _______________ from the proteins made by _________ ribosomes. The rest of the ______ is called ____________ because it lacks ______________. The smooth ER makes ____________ and breaks down __________ substances. Packaging and Distribution of Proteins – _____________ that contain newly made proteins move through the ________________ from the ER to the __________ ______________, which is a set of _______________, membrane-bound ________ that serve as the _____________________ and ____________________ center of the cell. ____________ inside the Golgi apparatus ______________ the proteins. Then it encloses the modified ____________ in new _______________ that bud from the surface of the Golgi apparatus. Some of these new vesicles are ______________, which are small, spherical organelles containing ________________ ______________. The ______, __________ _____________ and ______________ work together in the production, packaging and distribution of proteins. Mitochondria Produce ATP Nearly all eukaryotic cells contain ____________________, which are an organelle that harvests ______________ from ________________ compounds to make _______, the main energy ______________ of cells. Some ATP is made in the _________________, but most ATP is made ___________ the __________________. Cells that have a high energy requirement, such as ______________ cells, may contain _____________ or _____________ of mitochondria. A mitochondria has two _______________. The outer membrane is ____________, but the inner membrane is greatly _____________. The two _____________ form two ______________ in which _______________ _______________ take place. Mitochondrial DNA – Mitochondria have ______ and ____________ and make some of their own ______________. Most mitochondrial proteins are made by free ____________ in the ________________. The fact that mitochondria contain their own ______, which is similar to the circular DNA of _______________ cells, reflects the theory that primitive _____________ are the _____________ of mitochondria. Plant Cells Contain Structures that Animal Cells Lack All the organelles described so far are found in both ____________ cells and __________ cells. Plant cells have __________ additional structures. Cell Wall – The cell ______________ of a plant is surrounded by a thick ________ ________, which _______________ and ______________ the cell. Although the cell wall surrounds the cell _______________, it does not prevent the ________________ of substances across the cell membrane. It is made of a mixture of ______________ and __________________, including the polysaccharide _______________. The cell wall helps to support and maintain the cell’s _____________, protects from cell ______________, and _____________ the cell to adjacent cells. Chloroplasts – These are _______________ that use ____________ energy to make ____________________ from _____________ _____________ and ____________. Plants use carbohydrates to make other ______________ _______________ that are provide the energy for __________________. Chloroplasts are found in a wide variety of eukaryotic ___________ like ________________. Some scientists think that plants have evolved from a _____________ ____________. They supply much of the _____________ needed to power the ________________ of plant cells. Central Vacuole – Much of a plant cell’s volume is taken up by a large, membrane-bound space called the _____________ _______________. Vacuoles are found in both __________ and ____________ cells, but only __________ cells contain a ____________ ____________. The central vacuole _____________ ____________ and may contain many substances, including ________, _________________, and _____________. When the central vacuole is full, it presses the ________________ against the ______ _______ and make the cell ____________, enabling it to ____________ ______________. (This is why plants wilt and droop when they don’t get enough water.)