* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operant Conditioning Powerpoint
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Introspection illusion wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive flexibility wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive interview wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Piagetian theories of cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive semantics wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Theory of mind in animals wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Background music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Play (activity) wikipedia , lookup
Situated cognition wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive model wikipedia , lookup
Animal psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Animal culture wikipedia , lookup
Edward Thorndike wikipedia , lookup
Conditioned place preference wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
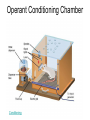
Operant Conditioning Terms Edward Thorndike • Law of Effect: behavior followed by favorable consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely (basis of Operant Conditioning) Cat Puzzle Skinner Box – a chamber containing a bar that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; devices are attached to record the animal’s rate of bar pressing •Skinner Box Video Operant Conditioning Chamber Conditioning Shaping • an operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of a desired goal “Good job” when they get on all fours SHAPING DEMO Give them a candy when they start crawling toward you Hug and a kiss when they stand up Types of Reinforcers Primary Reinforcer • An innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need CONDITIONED (SECONDARY) Reinforcer • a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer Cognitive Map • A mental representation of the layout of one’s environment Latent Learning • learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect • the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do Cognition and Biology • Cognitive Processes of Operant Conditioning • Cognitive processes are also at work in operant learning – Animals on a fixed-interval reinforcement schedule respond more frequently as the time gets closer to the reinforcer (EXPECTATIONS) • Biological Predispositions of Operant Conditioning • It is easier to reinforce behaviors normally associated with their natural behaviors – Example – can use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to rear up, more difficult to use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to wash its face