* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Behavioral Modification
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Social Bonding and Nurture Kinship wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
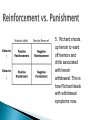
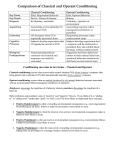
Amanda Morgan Fall 2011 • At the end of this lesson, students should be able..... to apply the terms and processes used in classical and operant conditioning to analyze examples of operant conditioning to recognize the real-world applications of classical and operant conditioning to design a behavior-modification program using operant conditioning Design program: Specify your target behavior Determine initial level of response Select strategies to increase/ decrease response strength Execute and evaluate your program Bring your program to an end Rough draft due in section for Peer-Review: 11/6/12 Final copy due: 11/21/12 (in lecture) 25 points 4 double-spaced pages (max) excluding graphs History of Classical Conditioning: ◦ Pavlov’s Dogs chini3.quangcaophuyen.net metronome metronome Extinction Acquisition Spontaneous recovery Renewal effect Acquisition of fears and phobias Advertising The office: http://vimeo.com/5 371237 mediabistro.com Focus of Operant Conditioning is on the CONSEQUENCE, whereas the focus of Classical Conditioning is on the PAIRING of the stimuli. Behavior ----> Consequence Big Bang Theory Video • An outcome or consequence of a behavior that strengthens the probability of the behavior. Positive reinforcement: Presentation of a stimulus that strengthens the probability of the behavior Negative reinforcement: Removal of an aversive stimulus that strengthens the probability of the behavior • Outcome or consequence of a behavior that weakens the probability of the behavior. Positive Punishment: The presentation of an aversive stimulus following a behavior, resulting in a decreased frequency of that behavior. Negative Punishment: The removal of a stimulus the organism wishes to experience following a behavior that results in a decreased frequency of that behavior. Consequences determined by function ($ not a reinforcer if it doesn’t increase behavior) Positive vs. Negative We need to determine 2 things: ◦ 1: What is the target behavior? ◦ 2: Who is doing the behavior? Behavior ↑ Behavior ↓ Audrey is complimented by her supervisor for submitting her report by the deadline. Diane begins working harder to submit her reports by the deadlines. Behavior ↑ Behavior ↓ Leon goes to the health club for a rare workout and pushes himself so hard by running 6 miles that his entire body aches and he throws up. Leon hasn’t run much since that workout. Behavior ↑ Behavior ↓ Sharron lets her dog out so she won’t have to listen to its whimpering. Now Sharron lets her dog out every time it begins to whimper so she doesn’t have to listen to it. Problems with punishment according to Skinner and others: ◦ Tells the organism only what not to do, not what to do ◦ Often creates anxiety, which can interfere with future learning ◦ May encourage people to become sneakier about displaying forbidden behavior ◦ Coming from parents, may provide a model for children’s aggressive behavior • Many behaviors are too complex to simply give out a reinforcement and expect the subject to learn exactly what you want them to. Shaping is a process of conditioning a target behavior by progressively reinforcing behaviors that come closer and closer to the target behavior. Activity Fixed ratio (FR)- after (n) number of responses Fixed interval (FI)- for the first response after a specified amount of time has passed Variable ratio (VR)- after a specific number of responses on average ◦ it is an average of the pre-determined number of responses, so actual number each time will vary randomly Variable interval (VI)- for the first response after an average length of time passes ◦ it is an average of the pre-determined length of time, so actual length each time will vary randomly 1. Sarah is paid on a commission basis for selling computer systems. She gets paid for every third sale. 2. Juan’s parents let him earn some pocket money approximately once a week by doing yard work. 3. Martha is fly-fishing. Think of each time that she casts her line as the response that may rewarded. 4. Jamal, who is in the fourth grade, gets a gold star from his teacher for every book he reads. 5. Skip, a professional baseball player, signs an agreement that his salary increases will be renegotiated every third year. Operant Classical ◦Elicited automatically ◦Provided unconditionally ◦Autonomic nervous system Target behavior is… Reward Behavior is… depends primarily on… ◦ Emitted voluntarily ◦ Contingent on behavior ◦ Skeletal muscles 1. Pick a behavior Not a behavioral chain Record modified frequency (and make a graph) 2. Observe that behavior Record unmodified frequency (and make graph) 3. Design a program Positive/Negative, Reinforce/Punish Fixed/Variable, Ratio/Interval Rationale 4. Implement that program 5. Observe the effect Analyze: Did it work? Why/Why not? What would have worked better? (revised program) What did you learn about yourself? Get with a partner Discuss 2-3 possible behaviors you would like to change (could be things you want to increase or decrease) Discuss whether you would choose positive/negative reinforcement/punishment Make this a meaningful assignment by choosing something you are actually interested in changing! Lilienfeld, S., Lynn, S., Namy, L. & Woolf, N. (2011). Psychology: From inquiry to understanding. Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon. Malott, R. (2008). Principles of Behavior. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall Adapted from previous lesson plans by Amanda Morgan (Psychology 111) Behavior ↑ Behavior ↓ 1. Jose drives fast and gets a speeding ticket, which costs him $130. Jose doesn’t speed much anymore. Behavior ↑ Behavior ↓ 5. Richard shoots up heroin to ward off tremors and chills associated with heroin withdrawal. This is how Richard deals with withdrawal symptoms now.