* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Weekly PowerPoint
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
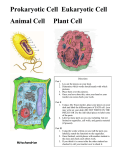
DO NOW Monday 10/17 Considering the benchmark scales, try to fill in the blanks. Large Scale: Body of an adult cow Macroscopic Scale: Liver Microscopic Scale: Atomic Molecular Scale: Happy Monday! • Pre-assessment: Cell Structure and Function – What do you already know? Impress me with your memory! – Need a hint? Who has them, what are they, where are they found, when are they made, what is their purpose? • A really cool video – What were some ideas about cells from the video that confirmed what you know about cells? – What is something new that you took away from watching this video? – What was the most surprising part about the video you just watched? • The Cell Coloring Diagram: Structures and Analysis DO NOW Tuesday 10/18 List 5 organelles or cell structures from your coloring sheet. Try to do this from memory first and then if you need, refer back to your sheet. *Get out your coloring sheet for completion stamps Happy Tuesday! • Log onto the computer at the lab station • Open an internet browser (Chrome or Internet Explorer) • Search for “SEPUP Cell Simulation” and click on the first result • OR type in the web address for the cell simulation http://sepuplhs.org/high/sgi/teachers/cell_sim.html • Using the cell simulation, build a plant and animal cell and use that information to complete the table for Part A. • • Be sure to click on each organelle or cell structure once you have placed it in your cell to receive a more detailed explanation of what it does (this will help you when completing the table). After completing the table in Part A, use that information to complete Parts B and C (back of the worksheet) Assigned: Cell Structure and Function Worksheet, if not completed during class, due beginning of class Wednesday (10/19) • Select an organelle, cell structure, or cell function You must receive approval from the teacher before beginning work on your presentation. First-come-first-served basis. • You will be creating a 90 second “commercial” for your organelle, structure, or function • Your group’s presentation must include the following: • Name of the organelle, cell structure, or cell function • Detailed description of what it does for the cell and why it is important to the organism as a whole • Selling point telling us why your organelle/structure or function is THE most important! – (Get creative! Really try to sell the class on why they should vote for your organelle, structure, or function) • (Optional) A disease, disorder, or condition related to your organelle, cell structure, or cell function (include a brief description: make sure the connection is clear) Happy Wednesday! • No DO NOW Write: Organelle/Structure Commercials • Sit near your group members • You will have 5 minutes to meet with your group and practice your 90 second (maximum) commercial – You may use notes during your presentation • During the commercial break, be sure to make note of which 2 organelle or cell structure commercials you liked best! *Turn Cell Structure and Function Worksheet into the green box before you leave class today • Your group’s presentation must include the following: • • • • Name of the organelle, cell structure, or cell function Detailed description of importance to cell and whole organism Selling point A disease, disorder, or condition (Optional) Let your voice be heard! Submit your ballot to the green box before you leave! Be sure to submit the Cell Structure and Function Worksheet before you leave class today DO NOW Thursday 10/20 Briefly explain the main function for the following organelles or cell structures: Cell Wall: Cell Membrane: Nucleus: Components of the Cell System Structures and their Functions 1. Cell Membrane Outside boundary of cell Double layer of FAT molecules (“phospholipid bilayer”) Proteins embedded within; have different functions Protects cell and regulates what enters and exits Does form seem to fit function? 2. Cell Wall Plants, some fungi, some bacteria, some protists have this Outside of membrane Provides structure Made of carbohydrates (mainly cellulose, which we know as fiber) Does form seem to fit function? Holds DNA and controls the cells activities. Does form seem to fit function? 3. Nucleus Pores in the nuclear membrane control flow of materials in and out. 3.5 Nucleolus Region within the nucleus where ribosomes are formed 4. Cytoplasm Present in all cells Jelly-like mixture of water, proteins, salt and sugar AND organelles. Does form seem to fit function? The Organelles Smaller, specialized compartments within a cell 5. Mitochondria Where energy stored in food is converted for use in the cell Number of mitochondria in a cell depends on the purpose of the cell Muscle cells Skin cells Does form seem to fit function? Many reactions happen at the inner membrane. Tagged/dyed mitochondria in a cell Tagged/dyed microtubules in a cell 6. Chloroplasts Chlorophyll - green pigment that allows photosynthesis Inside, contains flattened sacs “thylakoids”, where photosynthesis occurs Only in plants… though bluegreen pigment like chlorophyll found in some bacteria Photosynthesis reactions happen at the inner membrane. Does form fit function? 7. Ribosomes: Not compartments! No membrane Composed of two subunits Protein structures where more proteins are made The most abundant of all cell parts Do characteristics seem to fit function? 8. Endoplasmic Reticulum A large network of membranes that acts like a highway to allow molecules to move throughout cell Vesicles break off ER to transmit substances around cell Two types… Does form seem to fit function? 8a. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Studded with ribosomes! Processes proteins to export from the cell 8b. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum No ribosomes! Makes lipids (fats and steroids) Detoxification in liver cells 9. Golgi Bodies/Apparatus System of flattened sacs called cisternae Works with the RER to modify, package and release proteins Spawns vesicles to transport materials to the cell membrane Does location seem to fit function? 10. Vacuoles In plant cells: large and used for water + nutrient storage In animal cells: small and numerous and contain a variety of substances Does form seem to fit function? 11. Lysosomes Small, abundant sacs Contain chemicals for digesting waste, toxins, or useless organelles Formed from Golgi Common in animal and fungus cells Why do fungal and animal cells tend to have more lysosomes? How do we know all of this? The Cell Theory, developed in 1839 The microscope opened a world of discovery of life never seen before. By 1839, scientists Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann and Rudolf Virchow concluded the following as the…. The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3. All cells come from other cells. DO NOW Friday 10/21 Which of the cell parts is associated with the production of protein? Happy Friday! • Today you will be viewing different types of cells at the microscopic level. – Select 3 of the 5 different cells available and view them under a microscope. – Draw a picture in the space provided of what you see at 4X, 10X, and 40X magnification Do’s and Don’ts of Compound Microscopes HOW TO HANDLE A MICROSCOPE: A compound microscope should be treated as a VERY, VERY, VERY fragile piece of equipment. 1. Adjustments should be made gently and with finesse. 2. ALWAYS use both hands when picking the microscope up and moving it from one place to another. Do not drag it or push it on the countertop. 3. When focusing on a slide, ALWAYS start with the 4X red objective lens. Once you have the object in focus, then switch to the next higher power objective (10X yellow). Re-focus on the image and then switch to the next highest power (40X blue). NEVER advance more than one objective before focusing. 4. Use ONLY the fine focus control when focusing the higher power objectives (40X) on a slide. The coarse focus control is too coarse for focusing with these objectives. Objectives are fragile and must not be rammed into slides. Be gentle! Check yo’self! (Is this what you saw?) Adipose (Fat) Cells Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells Plant (onion root) Cells Cheek Cells Different Types of Cells Today you looked at (at least) 3 types of cells. All of these cells were dead. However, most cells in your body are living and very busy. In your notebook, answer the following questions: 1. What do you think is going on inside of living cells? 2. What do they need to do that? Compare the following types of cells (not all cells look exactly the same! Note-they are not all magnified to the same scale, so even though they look like they are different sizes, it is impossible to tell from these pictures) Intestinal cell Muscle cell Red blood cells Nerve cell (neuron) 3. What differences do you notice? 4. List any reasons why you think the structure is the way it is for each cell type. Complete the exit ticket and submit to green box before you leave! Enjoy the weekend!