* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microarrays - TeacherWeb
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
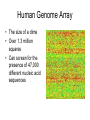
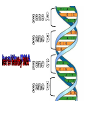
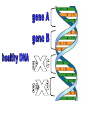
Microarrays Gene Expression • Except gametes, every one of our cells contains 46 chromosomes. • There are about 30,000 genes found on these chromosomes. • Some genes are active on every chromosome in every cell. • Some genes are active only in certain cells Normal Male Karyotype Normal Male Karyotype PINK1 gene – Active in every cell in the body CASQ2 gene – Active in only cardiac muscle cells ACTA1 gene – Active in skeletal muscle cells Changes in Gene Expression • May be caused by the environment • May indicate disease progression • May highlight differences among individuals What’s a microarray? • Allow scientists to analyze the expression of many genes in a single experiment. What does it do? • Compare gene expression in healthy and sick people • Compare gene expression of the same organism during different life stages • Compare gene expression of the same organism in different environments How does it work? Single stranded probes search for complementary target sequences. Probe sequence target sequence What a microarray looks like • • • • Glass slide, silicon chip, or nylon membrane 1.25 cm x 1.25 cm checkerboard Each square is 11 micrometers by 11 micrometers Attached to each square are millions of copies of one of a single stranded DNA probe Human Genome Array • The size of a dime • Over 1.3 million squares • Can screen for the presence of 47,000 different nucleic acid sequences How to make a microarray? Patient 1: Patient 2: Microarray: Interpretation: Genes A and B are expressed in healthy people Genes B and D are expressed in sick people