* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sci8Un6#17ACell+structures
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
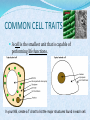
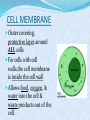
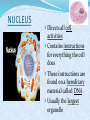
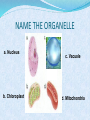
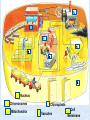
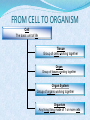
COMMON CELL TRAITS A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. In your NB, create a T chart to list the major structures found in each cell. COMPARING CELLS The size & shape of a cell relates to its function. (job it does) NB: Which cell has special extensions to carry electrical impulses? NB: Why do you think that red blood cells are round? CELL WALL protects the cell gives shape is made of cellulose A cell wall is found in plants, algae, fungi, & most bacteria. CELL MEMBRANE Outer covering, protective layer around ALL cells For cells with cell walls,the cell membrane is inside the cell wall Allows food, oxygen, & water into the cell & waste products out of the cell. CYTOPLASM gelatin-like inside cell membrane constantly flows NUCLEUS Directs all cell activities Contains instructions for everything the cell does These instructions are found on a hereditary material called DNA Usually the largest organelle Quick Check! Match the cell part to the job is does: A. Controls the cell B. Outer protective layer- in plants, not animals C. Controls what enters and leaves the cell D. Fills the cell, allowing chemical reactions to occur 2 1 3 4 CHROMATIN contains genetic code that controls cell made of DNA & proteins found in the nucleus MITOCHONDRIA Organelles that release energy from food This energy is released by breaking down food into carbon dioxide AKA the powerhouse b/c they release energy from food Some muscle cells have 20,000 mitochondria VACUOLES Temporary storage spaces Store food, water, waste Plant cells usually have larger vacuoles than animal cells CHLOROPLASTS Green organelles that make food found only in plant cells CHLOROPHYLL Found in chloroplasts A green pigment that gives leaves & stems their color Captures sunlight energy that is used to produce food called glucose Glucose is a type of sugar Quick Check! 2 Match the cell part to the job is does: A. Green pigment that traps light energy in plants B. Storage compartment C. Release energy for cell D. Contains genetic code or instructions E. Organelle that holds chlorophyll for food production in plants green material that fills the chloroplast 1 structure that holds chlorophyll 4 3 5 NAME THE ORGANELLE a. Nucleus b. Chloroplast c. Vacuole d. Mitochondria Compare Plant and Animal Cells Create a Venn Diagram to compare and contrast a typical Plant and a typical Animal cell. You must include the following: cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, chromatin, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplast, chlorophyll. Animal Cell Plant Cell 1- Nucleus 2- Chromosomes 3- Mitochondria 4- Ribosomes 4- Chloroplasts 5- Vacuoles 7- ER 6- Cell Membrane FROM CELL TO ORGANISM Cell The basic unit of life Tissue Group of cells working together Organ Group of tissues working together Organ System Group of organs working together Organism Any living thing made of 1 or more cells View this animation, paying attention to how each level builds on the one before it. Match the diagram to the level of organization: A. Atom 5 B. Molecule 1 C. Cell D. Tissue E. Organ F. Organ System 2 G. Organism H. Population 8 I. Community J. Ecosystem K. Biosphere Quick Check! 3 6 11 7 10 9 4