* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell race information cards
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
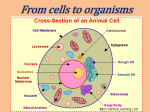
Animal Cell Animal cells are bounded by a cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances. The cytoplasm is the “factory” part of the animal cell in which chemical reactions take place to manufacture various substances. The nucleus holds the DNA molecules (chromosomes) that are composed of sections called genes. Gene code for the making of proteins that control the activity of the cell. Embedded in the cytoplasm are mitochondria- sausage shaped structures with a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. It is in the mitochondria that aerobic respiration (respiration that uses oxygen) takes place. Also in the cytoplasm of animal cells free or attached to membranes are ribosomes- small spherical structures that are where protein molecules are created using instructions supplied from the DNA in the nucleus. Plant Cell Plant cells are bounded by a cell wall made of cellulose fibres that forms a rigid box that although permeable to all but the largest molecules provides support for the cell and the plant as a whole. To the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances and is composed of proteins and phospholipids. The cytoplasm is the “factory” part of the plant cell in which chemical reactions take place to manufacture various substances. The nucleus holds the DNA molecules (chromosomes) that are composed of sections called genes. Genes code for the making of proteins that control the activity of the cell. Embedded in the cytoplasm are mitochondria- sausage shaped structures with a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. It is in the mitochondria that aerobic respiration (respiration that uses oxygen) takes place. Also in the cytoplasm of plant cells free or attached to membranes are ribosomes- small spherical structures that are where protein molecules are created using instructions supplied from the DNA in the nucleus. Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis in green plant cells. Vacuoles are fluid filled sac containing cell sap which are important in controlling water balance within the cell. Fungal Cell Fungal cells are bounded by a cell wall made of chitin that forms a rigid box that provides support for the cell. To the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances and is composed of proteins and phospholipids. The cytoplasm is the “factory” part of the fungal cell in which chemical reactions take place to manufacture various substances. The nucleus is the control centre of the cell. It holds the DNA molecules (chromosomes) that are composed of sections called genes. Gene codes for the making of proteins that control the activity of the cell. Embedded in the cytoplasm are mitochondria- sausage shaped structures with a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. It is in the mitochondria that aerobic respiration (respiration that uses oxygen) takes place. Also in the cytoplasm of fungal cells free or attached to membranes are ribosomes- small spherical structures that are where protein molecules are created using instructions supplied from the DNA in the nucleus. Vacuoles are fluid filled sac containing cell sap which are important in controlling water balance within the cell. Bacterial Cell Bacterial cells are bounded by a cell wall made of peptidoglycan that forms a rigid box that provides support for the cell. To the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances and is composed of proteins and phospholipids. The cytoplasm is the “factory” part of the bacterial cell in which chemical reactions take place to manufacture various substances. In a bacterial cell the DNA is free in the cytoplasm usually in one large mass. The DNA is composed of sections called genes. Genes code for the making of proteins that control the activity of the cell. In bacterial cells smaller circles of DNA called plasmids are found. Plasmids are freely exchanged between bacterial cells and are now used in “genetic engineering”. Also free in the cytoplasm of bacterial cells are ribosomes- structures that are where protein molecules are created using instructions supplied from the DNA. ribosomes cytoplasm cell membrane nucleus mitochondrion cell ribosomes mitochondrion membrane sap vacuole nucleus cell wall (cellulose) cytoplasm chloroplast ribosomes cell membrane cytoplasm vacuole nucleus mitochondrion cell wall (chitin) ribosomes cytoplasm plasmid cell membrane cell wall (peptidoglycan)