* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell structure
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
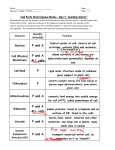
Cell structure Lecture 2 A. Cell Membrane – all cells a. FUNCTION- The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection and support b. Takes in water and food and eliminates waste c. STRUCTURE - The membrane is a double-layered sheet called a lipid bi-layer i. Polar heads face outwards and non-polar tails face inwards d. Embedded in the membrane are protein channels/pumps and carbohydrates B. Cell Wall – plants and bacteria a. Where is it found? i. Found in almost all prokaryotes ii. Found in plants, fungi, and algae iii. NOT found in animals b. Lies outside of the cell membrane c. Allow for movement of certain molecules i. Water, carbon dioxide, oxygen and some other substances d. The main function of the cell wall is to provide support and protection to the cell e. Structure - Cell walls are made of carbohydrates i.e. cellulose fiber C. Nucleus - eukaryotes a. Function - The nucleus controls most cell processes and contains the hereditary information of DNA b. Structure - Consists of 4 parts i. Nucleolus – small densely packed region where ribosomes are created ii. Nuclear Envelope – double membrane layer surrounding the nucleus iii. Nuclear Pores – a perforations within the nuclear membrane iv. Chromatin – this is the granular material within the nucleus 1. Chromosomes – the condensed form of chromatin just before a cell divides D.Cytoskeleton – all cells a.Function - A network of protein filaments that helps the cell keep its shape, also used in many forms of cell movement (in the documentary the virus traveled along these filaments) b.Structure - Made up of microtubules and microfilaments Ribosomes - eukaryotes i. Function Ribosomes assemble proteins following the coded instructions that come from the nucleus ii. Structure Ribosomes are made of protein and RNA b. Endoplasmic Reticulum - eukaryotes i. Function - The organelle in which components of the cell membrane are assembled and some proteins are modified Structure Types i. Smooth ER – contains collections of enzymes that perform specialized tasks, such as the synthesis of lipids (fats) ii. Rough ER – the part that is involved in the synthesis of proteins; has ribosomes embedded in the membrane c. Golgi Apparatus eukaryotes i. Function -Proteins made by the ER move to the Golgi apparatus where enzymes attach carbohydrates and lipids ii. Structure – folded sacs involved with modifying and packaging proteins d. Lysosomes – animal cells i. Structure - Are small organelles filled with enzymes ii. Main function is to break down lipids, carbohydrates and proteins into particles that can be used by the cells iii. Also helps to break down old organelles, remove debris from the cell e. Vacuoles – all cells i. Function Storage for the cell 1. Stores materials such as water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates ii. Plants have a single large vacuole (mostly water) f. Chloroplasts – plant cell Found in photosynthetic organisms i. Function - Use energy from sunlight to make energy-rich food molecules in a process known as photosynthesis ii. Structure – Light capturing pigment Contains thylakoids and chlorophyll iii. Contains its own DNA g. Mitochondria – eukaryotes i. Function Releases energy from stored food molecules in a process called cellular respiration ii. Found in eukaryotes iii.Structure – Small organelle that contains its own DNA (you get it from your momma) h. Organelle DNA i. Lynn Margulis suggested that mitochondria and chloroplasts were originally prokaryotic organisms that were enveloped by a eukaryotic cell ii. The DNA in mitochondria comes almost exclusively from the mother F. Movement through the membrane a. Facilitated diffusion – no energy required i. Molecules such as glucose sugar that cannot cross the cell membrane’s lipid bilayer directly can move through protein channels from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration with the concentration gradient b. Active transport – energy required i. When a molecule has to move against the concentration gradient ii. Each pump is used to move a specific molecule across the membrane 1. Example: sodium potassium pump moves sodium out and potassium in ( v. Endocytosis 1. The process of taking materials into the cell by means of infolding or pockets of the cell membrane vi. Exocytosis 1. The removal of large amounts of material from a cell exocytosis ANIMAL AND PLANT