* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle Krebs Cycle Oxidative Phosphorylation
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
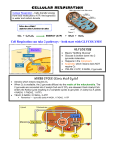
Pathway Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle Krebs Cycle Oxidative Phosphorylation Fatty Acid Cycle Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Site cytoplasm mitochondria mitochondria mitochondria Start Glucose Acetyl-CoA NADH or FADH2; H+, O2 Fatty Acid Activation 2 ATP End 2 Pyruvates Energy Production 2 NADH, 2 ATP (~ 6 ATP after ET) Pyruvate Aerobic: occurs in mitochondria Pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA + CO2 NADH (~ 3 ATP after ET) Acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs Cycle Anaerobic: occurs in cytoplasm Pyruvate + NADH → Lactate + NAD+ no ATP produced; makes NAD+ needed for glycolysis to continue Part of the Cori Cycle at right Anaerobic (yeast) Pyruvate → ethanol + CO2 2 ATP 2 ATP - once per fatty acid 2 CO2 NAD+, FAD, H2O Acetyl-CoA 3 NADH, FADH2, GTP (~ 12 ATP after ET) FADH2 = 2 ATP in ET NADH = 3 ATP in ET NADH produced in cytoplasm yields 2ATP NADH, FADH2 or (~ 5 ATP per cycle after ET) Cori Cycle: Glucose → Glucose The first half of the cycle occurs in many different tissues (like muscle) when lactate is formed from glucose during oxygen debt. Glucose → 2 Lactates Provides: 2 ATP from glycolysis The second half of the cycle converts lactate back into glucose. This takes place in the liver when plenty of oxygen (and energy) is available. 2 Lactates → Glucose Uses: 4 ATP, 2 GTP, 2 NADH (net cost is ~ 10 ATP) # cycles = # C's in fatty acid –1 2 Glycerol (from fat) Glycerol is converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate by oxidation and phosphorylation. Glycerol → Dihydroxyacetone phosphate glycerol is activated by using 1 ATP and the reaction produces 1 NADH (~ 2 ATP after ET - 1 ATP activation = 1 ATP) Dihydroxyacetone phosphate is then broken down in the second half of the glycolysis pathway Dihydroxyacetone phosphate → pyruvate making 2 ATP and 1 NADH (~ 4 ATP after ET)