* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1) Where does glycolysis occur in the cell
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
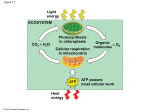
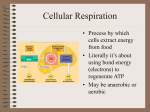
Will’s 2nd Pre-Test 1) Where does glycolysis occur in the cell? a) The cell membrane b) The Nucleus c) The cytoplasm d) The mitochondria 2) What is produced in Glycolysis in the absence of Oxygen? a) Pyruvate b) Lactate c) Glucose d) Protein 3) In a cell, most of the FADH2 production occurs ___________. a) on the surface of a ribosome. b) inside the nucleus. c) in the matrix of a mitochondrion. d) between the double membranes of a mitochondrion e) in the cytoplasm 4) At the end of the electron transport chain, the electrons __________. a) are transferred back to NAD+ to make NADH. b) are transferred back to FAD to make FADH2. c) combine with protons and oxygen to make water. d) combine with carbon and oxygen to make CO2. e) both A and B are correct. 5) During the Krebs Cycle, Pyruvate is ___________ to acetyl CoA. a) reduced b) oxidized c) eliminated d) transferred 6) _____________ is the main process of producing ATP in glycolysis. a) Substrate-level Phosphorylation b) Enzymatic-reduction of Pyruvate c) Reduction of Glucose d) Oxidative Phosphorylation 7) __________ are the portion of a gene sequence that hold the important information for coding genes. a) GC base pairs b) AT base pairs c) GT base pairs d) CA base pairs 8) All of the following processes occur within mitochondria except: a) the splitting of glucose b) the formation of citric acid c) the catabolism of citric acid to produce NADH, CO2, AND H+ d) the transfer of electrons form NADH to the electron transport chain e) the reduction of oxygen to form water. 9) Phosphorylation of ADP in the electron transport chain is powered by the movement of electrons through a(n) _______________. a) phospholipid b) ATP-synthase molecule c) ADP-protein carrier d) substrate-level phosphorylation 10) In order to fit into the nucleus of a cell, the DNA must _________ itself around small proteins called ___________. a) coil; histones b) unwrap; histones c) coil; polymerases d) unwrap; polymerases 11) How many amino acids are coded for by this mRNA? AUCATGCCCGGTAUGAUGACC a) 4 b) 7 c) 10 d) 13 e) 21 12) ___________are the super-coiled, dense form of DNA. a) chromatins b) genomes c) histones d) chromosomes 13) ______ nucleotide base(s) comprise a single codon, which codes for ___ amino acid. a) 1; 4 b) 2; 3 c) 3; 1 d) 3; 2 14) _____________ serves as the code for protein synthesis. a) DNA b) RNA c) ribosomes d) mitochondrion 15) The double helix of DNA supported by hydrogen bonds between the __________. a) sugar phosphate b) nitrogenous bases c) carboxyl bases d) water 16) Ketoacidosis generally occurs in ____________ by the formation of _____________. a) Type II Diabetes; ketone bodies b) Type I Diabetes; amides c) Type I Diabetes; ketone bodies d) Type I Diabetes; hydroxyl groups. 17) ____________ is your last resort for energy. a) glucose b) fats c) proteins d) water 18) Dangers of Ketoacidosis include all of the following EXCEPT: a) Blood pH rises b) Fruity smell of breath c) diabetic coma d) death 19) Transcribing mRNA from DNA requires ____________. a) DNA poymerase b) RNA polymerase c) DNA helicase d) protein kinase d) tRNA 20) During cellular respiration, energy is transferred to NAD+ and FAD in the form of _________. a) protons b) electrons c) heat d) ATP e) neutrons 21) Which of the following cells only gain energy STRICTLY via glycolysis? a) brain cells b) heart cells c) red blood cells d) kidney cells 22) Most of the energy produced in the production of ATP is lost in the form of _________. a) electricity b) heat c) protons d) none of the above; the process is 100% efficient 23) In the electron transport chain, __________ is the final electron acceptor. a) Carbon b) Hydrogen c) Water d) Oxygen 24) Without any oxygen, a cell can only yield a NET production of _______ ATP per molecule of glucose. a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 25) During the synthesis of proteins, ribosomes _____________. a) open DNA so it can be transcribed b) transcribe a sequence of mRNA c) translate a sequence of mRNA into a protein d) transport a particular amino acid during translation e) help proteins to fold after they are made. 26) In protein metabolism, most of the protein is converted into a) acetyl CoA b) acid c) uracil d) glucose 27) Which of the following can be used as a source of energy? a) carbohydrates b) fats c) proteins d) all of the above 28) ATP makes which one of the following processes possible? a) muscular contraction b) active transport c) homeostasis d) all of the above 29) Transcribe the following DNA sequence into mRNA: GGTATGCCCTACGCC A. GGTATGCCCTACGCC B. CCATACGGGATGCGG C. CCAUACGGGAUGCGG D. TTCCGCTTTGCGAATC 30) NAD+ and FAD are __________&_____________. a) coenzymes; carbohydrates b) coenzymes; temporary energy carriers c) substrates; carbohydrates d) substrates; temporary energy carriers Glycolysis - Occurs in the cytoplasm - Does not require Oxygen - Produces 2 pyruvate, 2 net ATP (4 total), and NADH Krebs Cycle - Occurs in the Matrix of the Mitochondria - Requires Oxygen - Produces 2 ATP, a whole buch on NADH & FADH2, and CO2 Electron Transport Chain - Occurs in the inner membrane of mitochondria - Requires Oxygen - Produces 34 ATP along with metabolic water