* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic Cells
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
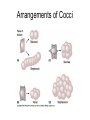
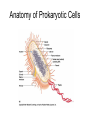
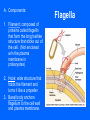
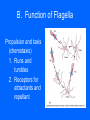
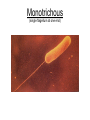
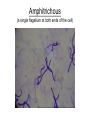
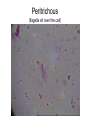
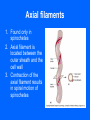
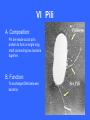
Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic Cells Chapter 4 Arrangements of Cocci Arrangements of Cocci Arrangements of Bacilli Arrangements of Bacilli Arrangements of Spiral Bacteria Arrangements of Spiral Bacteria Anatomy of Prokaryotic Cells • Glycocalyx: Capsule or Slime layer? • A. Components: sticky gelatinous polymer of polysaccharide and protein found on the outside of the cell wall. • 1. Thick, highly organized, and solidly fixed to the cell wall, it is referred to as a capsule. • 2. Thin layer, unorganized, loosely held to the cell wall it is referred to as a slime layer. Glycocalyx B. Function: 1. Attachment: Allows the bacteria to attach to surfaces in its natural environment. 2. Protection: 1. Protect against dehydration 2. Protects against phagocytosis 3. Nutrition: 1. Keeps nutrients in the cell. 2. May be a source of nutrition A. Components: 1. Filament: composed of proteins called flagellin that form the long hairlike structure that sticks out of the cell. (Not enclosed w/in the plasma membrane in prokaryotes) 2. Hook: wide structure that holds the filament and turns it like a propeller 3. Basal body anchors flagellum to the cell wall and plasma membrane. Flagella B. Function of Flagella Propulsion and taxis (chemotaxis) 1. Runs and tumbles 2. Receptors for attractants and repellant Types of Flagella Arrangement • Monotrichous: a single flagellum at one end • Amphitrichous: a single flagellum at both ends of the cell • Lophotrichous: two or more flagella at one or both ends of the cell. • Peritrichous: flagella all over the cell. Monotrichous (single flagellum at one end) Amphitrichous (a single flagellum at both ends of the cell) Lophotrichous (two or more flagella at one end of the pole) Peritrichous (flagella all over the cell) Axial filaments 1. Found only in spirochetes 2. Axial filament is located between the outer sheath and the cell wall 3. Contraction of the axial filament results in spiral motion of spirochetes Fimbriae A. Composition: Fimbriae are hairlike appendages made out of pilin (shorter, and thinner than flagella) B. Function Used for attachment and colonization of host. VI Pili A. Composition: Pili are made out of pilin protein to form a single long shaft connecting two bacteria together. B. Function: To exchange DNA between bacteria