* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Review
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Hippocampus wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
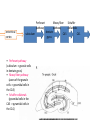
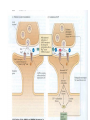
2nd half of the course • Spatial Processing • LTP Ongoing operation of the hippocampus and related brain structures during memory performance • functional neuroimaging methods in normal humans • recording of the activity patterns of single neurons in animals. Nature of the task: • Allocentric (world centered) processing • Egocentric (body centered) processing Critical structures in the memory system of the medial temporal lobe 1 2 the hippocampus the parahippocampal region Functional imaging studies of Human spatial navigation Hippocampus place cells in rats Initial report: fire only when the rat is in a particular location Recent analysis Navigation cues: • external landmarks • idiothetic (self-motion) cues Neural mechanisms: •Cell types Place cells: hippocampus head direction cells •Response properties for both types of cells Controlled by an interaction between landmarks and idiothetic cues Neural mechanisms (Con’t): Theory Place cells – cognitive map model Alterative theories: Eichenbaum “memory space” model o Place cell not exist and function together as a simple topography of external space as was originally suspected. o these cells fire in response to the complex interaction of multiple cues and not in response to an internal Cartesian coordinate system. LONG-TERM POTENTIATION (LTP) Anatomical background Hippocampal formation: two interlocking C-shaped regions (the hippocampus and the dentate gurus) main inputs to the hippocampal formation: entorhinal cortex via axon of the perforant pathway Hippocampus has three major afferent pathways Mossy fiber pathway Perforant pathway entorhinal cortex subiculum • Perforant pathway (subiculum -> granule cells in dentate gyrus) • Mossy fiber pathway (axons of the granule cells -> pyramidal cells in the CA3) • Schaffer collaterals (pyramidal cells in the CA3 -> pyramidal cells in the CA1) dentate gyrus CA3 Schaffer collaterals CA1 Underlying molecular mechanisms • LTP (in area CA1) depends on certain changes at glutamate synapses • LTP requires some sort of additive effect of highfrequency stimulation, •Activation of synapses and depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron must occur at the same time •Types of glutamate receptors •NMDA receptors •Non-NMDA receptors At NMDA receptors background 1. Controls a calcium ion channel 2. glutamate is neither excitatory nor inhibitory 3. Ion channel is blocked by magnesium ions DURING INDUCTION 1. Mg2+ removal 2. Ca2+ entry 3. After induction of LTP, transmission at non-NMDA receptors is facilitated (entry of Na+) Inside the cell 1. Ca2+ activates some protein kinases (catalyze phosphorylation) 2. Calcium-calmodulin kinase (CaM kinase) 3. The activated protein kinases also trigger the synthesis of proteins 1. activate cAMP responsive element-binding protein (CREB) 2. CREB -> production of the transcription (mRNA) of IEGs -> regulate the expression of particular late effector genes (LEGs) -> synthesis of proteins 4. Induction of LTP requires a retrograde signal, from the postsynaptic neuron to the presynaptic neuron LINKS BETWEEN LTP AND LEARNING AND MEMORY Molecular Approaches NMDAR-dependent LTP - spatial learning in the water maze? Water maze overall performance (Morris et al, 1986) Partition of the task into two components (Bannerman et al, 1995) Non-spatial pretraining and Spatial training Gene knockout mutants (NMDAR) Gene disruption at embryotic stage (early studies) mutants with effects that are regionally and temporally restricted Electrophysiological Approaches Does learning produce LTP-like changes? skilled learning (Rioult-Pedotti, 1998, 2000) Does induction of LTP influence learning? prior to learning (to saturate normal LTP) (Moser, 2000)