* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzyme-linked secondary antibodies
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial microcompartment wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
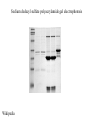
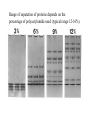
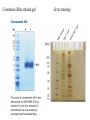
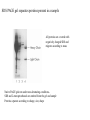
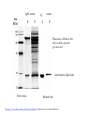
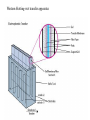
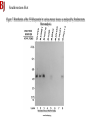
Lab 6. Preparation of rabbit IgG Enzyme linked Immunosorbent Assay Variations in the ELISA technique Used for testing the amount of antibody to an antigen in serum Add the solution containing antigen to be measured The sensitivity of the Sandwich ELISA is dependent on four factors: 1. The number of molecules of the first antibody that are bound to the solid phase. 2. The avidity of the first antibody for the antigen. 3. The avidity of the second antibody for the antigen. 4. The specific activity of the enzyme attached to the second antibody. http://www.chemicon.com/resource/ANT101/a2C.asp Antibody titres are worked out empirically. Try several dilutions of antibody 1:250/ 1:500/ 1:1000/ 1:10,000 Dilutions of known Standard Always do duplicates of each test Cannot just take the Ab concentration from a different protocol Ideally the enzyme substrates should be stable, safe and inexpensive. Popular enzymes are those which convert a colorless substrate to a colored product, e.g. p-nitrophenylphosphate (pNPP) which is converted to the yellow p-nitrophenol by alkaline phosphatase. ELISPOT Assay E=enzyme CS-chromogenic substrate Kuby 6-11 CP-coloured pdt Sensitivity of the ELISPOT assay. The specified number of IFN--producing T cells was mixed into one million antigen presenting cells (APC). The number of IFN--producing cells was measured by ELISPOT (upper panel) and intracytoplasmic staining (middle panel); results of ELISA measurements are shown in the lower panel. http://www.elispot-analyzers.de Spot size is proportional to secretion •High-throughput. •Fewer cells are required compared to other cellular assays. •Lymphocytes survive the testing in ELISPOT assays. SDS covers proteins in a net negative charge Addition of 2-mercaptoethanol reduces disulphide bonds and Boiling is used to further denature proteins. + Charged R groups +H + - + + H + Hydrophobic areas - - - - - - Before SDS - -- Migrate in gel according to mass - - - - - Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Wikipedia Range of separation of proteins depends on the percentage of polyacrylamide used (typical range 12-16%). Proteins are separated in a ‘discontinuous’ system. Stacking gel has looser pores to allow proteins to line up first. How does an SDS-PAGE gel really work? http://mullinslab.ucsf.edu/Protocols%20HTML/SDS _PAGE_protocol.htm How the discontinuous gel works. pH 6.8 Glycine Proteins ClpH 8.8 Leading ions Glycine –ve charge + Coomassie Blue stained gel silver staining Western blots- Ab used to identify Ag immobilized on nylon SDS PAGE gel separates proteins present in a sample All proteins are covered with negatively charged SDS and migrate according to mass Native PAGE gels run under non-denaturing conditionsSDS and 2-mercaptoethanol are omitted from the gel and sample Proteins separate according to charge, size, shape IgM serum Ig serum What does a Western blot tell you that a protein gel does not? mAb detects light chain Silver stain Western blot Bromage, E. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 Jan;143(1):61-9. Epub 2005 Dec 1. Protein blotting Two major factors affect the efficiency 1. 2. The elution from the gel -use the lowest percentage of acrylamide that will allow resolution -high molecular weight proteins blot poorly Efficiency of binding to the membrane - nitrocellulose (not covalently bound) - Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) - Activated nylon Transfer of proteins to the membrane Western blotting-wet transfer apparatus Western blot-semi-dry transfer of proteins Detection Primary antibody followed by: Radioactive-labelled 125 I staphlococcal protein A or streptococcal protein G Enzyme-linked secondary antibodies -horseradish peroxidase (HRP) -alkaline phosphatase-BCIP/NBT BCIP (5-Bromo-4-Chloro-3'-Indolyphosphate p-Toluidine Salt) and NBT (Nitro-Blue Tetrazolium Chloride). Chemiluminescent detectionHRP catalyzes the oxidation of luminol in hydrogen peroxide. Luminol decays by light emission. AP catalyzes the dephosphyorylation of adamantyl-1-2-dioxetane phosphate, resulting in emission of light. Can see proteins that are not normally visible Far western technique Detection of protein-protein interactions using a labelled bait protein Southwestern blot Figure 7 Distribution of the 52 kDa protein in various mouse tissues as analysed by Southwestern blot analysis Biochemical Journal (1998) 329, 623-629 www.biochemj.org