* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jezequel_Inside the Cell Notes-1gh2ogo
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
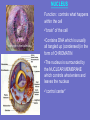
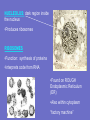
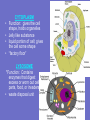
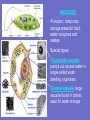
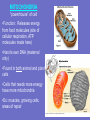
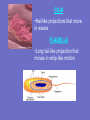
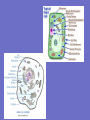
Inside the Cell Unit 2: The Cell • EUKARYOTES: organism whose cells contain a – Membrane-bound nucleus – Other organelles • PROKARYOTES: unicellular organism that lacks a membranebound nucleus • Lack other cell organelles • Example: bacteria, blue-green algae Organelle: cell component that performs specific functions for the cell NUCLEUS Function: controls what happens within the cell •“brain” of the cell •Contains DNA which is usually all tangled up (condensed) in the form of CHROMATIN •The nucleus is surrounded by the NUCLEAR MEMBRANE which controls what enters and leaves the nucleus •“control center” NUCLEOLUS: dark region inside the nucleus •Produces ribosomes RIBOSOMES •Function: synthesis of proteins •Interprets code from RNA •Found on ROUGH Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) •Also within cytoplasm “factory machine” • • • • CYTOPLASM Function: gives the cell shape, holds organelles Jelly like substance liquid portion of cell; gives the cell some shape “factory floor” LYSOSOME *Function: Contains enzymes that digest excess or worn out cell parts, food, or invaders • waste disposal unit ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) •Function: delivery system for cell •Folded membrane forming a network of connected tubes •Rough ER: studded with ribosomes, transports proteins •Smooth ER: has no ribosomes VACUOLES •Function: temporary storage areas for food, water, enzymes and wastes Special types: •Contractile vacuole: pumps out excess water in single-celled water dwelling organisms •Central vacuole: large vacuole found in plants, used for water storage GOLGI APPARATUS •Function: Stores and distributes materials into vacuoles •Stacked, flattened sacs “assembly line”— customization shop for finishing touches before leaving the factory MITOCHONDRIA “powerhouse” of cell •Function: Releases energy from food molecules (site of cellular respiration, ATP molecules made here) •Has its own DNA (maternal only) •Found in both animal and plant cells •Cells that needs more energy have more mitochondria •Ex: muscles, growing cells, areas of repair CHLOROPLASTS •Function: Site of photosynthesis •Found in plant cells (not animal cells) •Contains pigment called chlorophyll CYTOSKELETON CYTOSKELETON Function: *Forms framework to help maintain shape *Tiny rods that crisscross the cell *May be microfilaments or microtubules CILIA •Hairlike projections that move in waves FLAGELLA •Long tail-like projection that moves in whip-like motion Review the Parts • http://www.johnkyrk.com/CellIndex.html