* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Movement Through the Cell Membrane
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
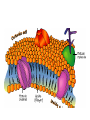
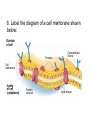
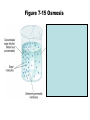
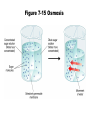
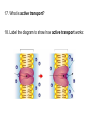
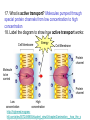
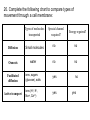
Movement Through the Cell Membrane 1. Review: What are the building blocks of lipids? 2. Sketch a lipid molecule in the space below. Label your sketch! 1. Review: What are the building blocks of lipids? Glycerol and fatty acids 2. Sketch a lipid molecule in the space below. Label your sketch! 1. Review: What are the building blocks of lipids? Glycerol and fatty acids 2. Sketch a lipid molecule in the space below. Label your sketch! Fatty Acids Glycerol 3. What is the function of the cell membrane? 4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer. 5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane. a. _____________ b. _______________ 3. What is the function of the cell membrane? Regulate what enters and leaves the cell; protect and support the cell 4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer. 5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane. a. _____________ b. _______________ 3. What is the function of the cell membrane? Regulate what enters and leaves the cell; protect and support the cell 4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer. Double-layered sheet of lipid molecules; hydrophilic heads point out, hydrophobic tails point in 5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane. a. _____________ b. _______________ 3. What is the function of the cell membrane? Regulate what enters and leaves the cell; protect and support the cell 4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer. Double-layered sheet of lipid molecules; hydrophilic heads point out, hydrophobic tails point in 5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane. a. proteins b. _______________ 3. What is the function of the cell membrane? Regulate what enters and leaves the cell; protect and support the cell 4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer. Double-layered sheet of lipid molecules; hydrophilic heads point out, hydrophobic tails point in 5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane. a. proteins b. carbohydrates http://www.sciencefriday.com/videos/watch/10210 6. Label the diagram of a cell membrane shown below: Outside of cell Proteins Carbohydrate chains Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer 7. Define the following terms: a. solution: b. solute: c. solvent: d. concentration: 7. Define the following terms: a. solution: mixture of 2 or more substances in which molecules are evenly distributed b. solute: c. solvent: d. concentration: 7. Define the following terms: a. solution: mixture of 2 or more substances in which molecules are evenly distributed b. solute: substance that is dissolved in a solution c. solvent: d. concentration: 7. Define the following terms: a. solution: mixture of 2 or more substances in which molecules are evenly distributed b. solute: substance that is dissolved in a solution c. solvent: substance in which the solute is dissolved d. concentration: 7. Define the following terms: a. solution: mixture of 2 or more substances in which molecules are evenly distributed b. solute: substance that is dissolved in a solution c. solvent: substance in which the solute is dissolved d. concentration: mass of solute in a given volume of solution 8. During the process of diffusion, molecules tend to move from to until the solution reaches equilibrium. 9. Does diffusion require energy? _______ Explain. 8. During the process of diffusion, molecules tend to move from an area of high concentration to until the solution reaches equilibrium. 9. Does diffusion require energy? _______ Explain. 8. During the process of diffusion, molecules tend to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the solution reaches equilibrium. 9. Does diffusion require energy? _______ Explain. 8. During the process of diffusion, molecules tend to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the solution reaches equilibrium. 9. Does diffusion require energy? __NO__ Explain. Molecules naturally move from HIGH concentration to LOW concentration Example of Diffusion: • The smell of popcorn after it’s been popped. • Does the smell of popcorn stay where the popcorn was popped? Why or why not? 10. Why are biological membranes described as selectively permeable? 11. What is osmosis? 10. Why are biological membranes described as selectively permeable? Some substances can pass through the membrane while other substances cannot 11. What is osmosis? 10. Why are biological membranes described as selectively permeable? Some substances can pass through the membrane while other substances cannot 11. What is osmosis? Diffusion of water across a membrane 12. Label the drawing below to show how osmosis works. water Cell Membrane glucose Figure 7-15 Osmosis Figure 7-15 Osmosis 13. Define the following terms: a. hypertonic: b. hypotonic: c. isotonic: 14. Cells are almost always __________ to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water ____ the cell. Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. b. 13. Define the following terms: a. hypertonic: Solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell • Water leaves the cell, animal cells can shrink. b. hypotonic: lower concentration of solute • Water enters the cell, animal cells can expand and possibly burst. • Plant and bacteria cells have their cell walls that provides provide protection from too much osmotic pressure Isotonic • The concentration of the solutes is the same inside and outside the cell. • Water goes in and out at the same rate and pressure doesn’t change 14. Cells are almost always __________ to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water ____ the cell. Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. b. 14. Cells are almost always hypertonic to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water ____ the cell. Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. b. 14. Cells are almost always hypertonic to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water into the cell. Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. b. 14. Cells are almost always hypertonic to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water into the cell. Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. cell walls keep cell from expanding b. 14. Cells are almost always hypertonic to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water into the cell. Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. cell walls keep cell from expanding b. contractile vacuole pumps extra water out of cell http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OYoaLzobQmk 15. What is facilitated diffusion? 16. Label the diagram to show how facilitated diffusion works: 15. What is facilitated diffusion? Diffusion of molecules across a cell membrane through a special protein channel 16. Label the diagram to show how facilitated diffusion works: Protein channel Glucose molecules High concentration of solute Low concentration of solute Cell Membrane http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_facilita 17. What is active transport? 18. Label the diagram to show how active transport works: 17. What is active transport? Molecules pumped through special protein channels from low concentration to high concentration 18. Label the diagram to show how active transport works: Cell Membrane Energy Cell Membrane Protein channel Molecule to be carried Protein channel Low High concentration concentration http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_the_s 19. Define the following terms: a. endocytosis: b. phagocytosis: c. exocytosis: 19. Define the following terms: a. endocytosis: process of cellular ingestion by which the cell membrane folds inward to bring substances into the cell. b. phagocytosis: c. exocytosis: 19. Define the following terms: a. endocytosis: process of cellular ingestion by which the cell membrane folds inward to bring substances into the cell. b. phagocytosis: (another name for endocytosis) c. exocytosis: 19. Define the following terms: a. endocytosis: process of cellular ingestion by which the cell membrane folds inward to bring substances into the cell. b. phagocytosis: (another name for endocytosis) c. exocytosis: removal of material from a cell; membrane surrounding material fuses with cell membrane to force material out 20. Complete the following chart to compare types of movement through a cell membrane: Types of molecules transported Diffusion Small molecules Special channel required? Energy reguired? no no Osmosis water no no Facilitated diffusion ions, sugars (glucose), salts yes no ions (H+, K+, Na+, Ca2+) yes Active transport yes