* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide Answers
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
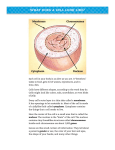
ANSWERS TO STUDY GUIDE 1A. Cell membrane 1B. Cell wall 1C. Cytoplasm 1D. Vacuole 1E. Nucleus 1F. Chloroplasts 1G. Cytoskeleton 1H. Mitochondria 1I. ER 1J. Golgi bodies 2. Cell wall and chloroplasts 3. Organelle Nucleus Nucleolus Cell wall Vacuole Function Control center Houses DNA Helps plant cells be rigid Controls what goes in/out of cell Site of photosynthesis – contain chlorophyll Holds organelles in place Powerhouse – converts food into energy Storage facility Lysosome Ribosome Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Body Clean up crew Makes proteins Transports materials Sort proteins Cell membrane Chloroplasts Cytoplasm Mitochondria Plant or Animal? Both Both Plant Both Plant Both Both Both, but plant cells have only one large vacuole Both Both Both Both 4a. 4b. 4c. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of organization in organisms. All cells come from cells. 5. The movement of substances through the cell membrane without the use of energy. 6. diffusion Osmosis Facilitated diffusion 7a. 7b. diffusion When particles move from high to low concentrations 8. to reach equilibrium – where there are the same # of particles outside as inside the cell 9. the diffusion of water through a cell membrane 10. Molecules can move into/out of cell with the help of a transport protein. 11. When energy is used to move materials across the cell membrane – 2 types are endocytosis (into) and exocytosis (out of) 12. Endocytosis – into the cell Exocytosis – out of the cell Both deal with moving large particles 13. process in which the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei – happens in body cells 14. Stages of mitosis – IPMAT Interphase – chromosomes duplicate Prophase – chromatid pairs visible and spindle fibers form Metaphase – chromatid pairs line up in center (MIDDLE) of cell Anaphase – chromatids separate Telophase – cytoplasm separates Last Phase – Cytokinesis – two new cells are formed 15. two new nuclei that are identical to each other and the original nucleus 16. Cell division producing haploid sex cells Different because two divisions of the nucleus occur – like mitosis x2. Deals with sex cells – egg and sperm Also, know the following: Type of Cell Division Type of cells # of chromosomes/pairs Product (result) In humans…. In fruit flies…. In tomatoes… Mitosis Meiosis Somatic (body) Gametes (sex) Sperm=male Egg=female Haploid (half) Diploid (double) 2 identical daughter cells 46 chromosomes 8 chromosomes 24 chromosomes 4 identical gametes How many pairs? 23 How many pairs? 4 How many pairs? 12