* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 4 overview
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
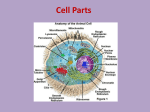
UNIT 4 OVERVIEW: CELL BIOLOGY Central Idea(s): Cells were first observed using very primitive microscopes in the mid 1600s. Advances in technology have allowed greater insights into the intricate structure and function of cells. Today we know that a cell is the basic unit of life and that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Today we know that all cells have a purpose. Some cells carry oxygen while others fight disease. Some single- celled organisms such as protists sole function is to survive. In this unit you will learn about various cell types, their many different structures, and how they carry out many of life’s functions. TEXTBOOK – Chapter 7 and Section 8.1 Vocabulary and Key Terms prokaryote eukaryote cell theory plasma membrane semi- permeability phosopholipid bilayer hydrophobic hydrophilic Brownian motion concentration gradient dynamic equilibrium diffusion passive transport active transport transporter proteins channel proteins osmosis isotonic hypertonic hypotonic endocytosis exocytosis phagocytosis pinocytosis organelles nucleus nucleolus mitochondria Golgi apparatus endoplasmic reticulum ribosome chloroplast centrioles cilia and flagella food vacuole central vacuole vesicle lysosome cytoplasm cytoskeleton cell wall cellulose Objectives & Study Questions Cell Theory 1. What is the cell theory? 2. Who was the first to term the word “cell”? What did he observe? 3. How do prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes? Give examples of each. 4. What is the function of each of the following animal organelles? a. nucleus b. nucleolus c. mitochondria d. Golgi apparatus e. endoplasmic reticulum (ER) f. ribosomes g. chloroplasts h. cilia and flagella i. vacuole j. lysosomes Pioneer High School Biology 2011-2012 Murdock/Smith k. vesicles 5. Contrast the smooth ER and the rough ER. 6. Compare and contrast a plant cell and bacterial cell with an animal cell. 7. What important process occurs in chloroplasts? 8. What role do vacuoles play in plants? 9. What role does the cytoskeleton and cytoplasm play in a cell? 10. What role does a cell wall play in plant and bacterial cells? 11. Identify the parts of a cell from a diagram. 12. Explain the role of the nucleus, rough ER, Golgi apparatus and vesicles in making a protein. Plasma Membrane & Cell Transport 13. What is osmosis? 14. Differentiate solute and solvent. 15. Contrast isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions. 16. Explain what would happen to a cell if it were placed in a ... a. hypertonic solution b. hypotonic solution c. isotonic solution 17. Compare endocytosis with exocytosis. 18. Explain the structure of the plasma membrane. 19. Contrast the following pairs of terms: a. hydrophobic vs. hydrophilic b. polar vs. nonpolar 20. Explain the polarity of the plasma membrane (phosphate heads and lipid tails) 21. Define selective permeability 22. Contrast a concentration gradient with a dynamic equilibrium 23. Define active and passive transport. 24. Compare and contrast facilitated diffusion with active transport. 25. Explain the role of channel proteins and transport proteins in cell transport. CA State Standards: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. b. Students know how prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), and viruses differ in complexity and general structure. c. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. d. Students know the role of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the secretion of proteins. e. Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar from carbon dioxide. f. Students know the role of the mitochondria in making stored chemical-bond energy available to cells by completing the breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide. Pioneer High School Biology 2011-2012 Murdock/Smith