* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis Matching Worksheet
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
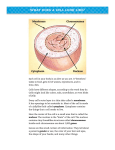
Name: _______________________________________ Block: ________ Date: ___________________ Mitosis Matching For each of the statements below indicate which part of the cell cycle it is referring to. Your choices are: interphase (I), prophase (P), metaphase (M), anaphase (A), telophase (T), cytokinesis (C). _______ 1. A nuclear envelope re‐forms around each cluster of chromosomes. _______ 2. The spindle begins to break apart. _______ 3. The chromosomes become visible. _______ 4. The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. _______ 5. The chromosomes continue to move until they have separated into two groups near the ends of the cell . _______ 6. Chromosome replication takes place. Because of this, each chromosome consists of two identical “sister” chromatids. _______ 7. The DNA starts to unwind in the nucleus. _______ 8. Periods of intense growth ‐ cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles. _______ 9. “In‐between” DIVISIONS ‐ A period of growth. _______ 10. Some cells can spend almost their entire life cycle in this phase (even 60 YEARS). _______ 11. The centromeres that joins the sister chromatids split, allowing the sister chromatids to separate and become individual chromosomes. _______ 12. The cell membrane is drawn inward until the cytoplasm is pinched into two nearly equal parts. This looks like an “8” in the animal cell. _______ 13. Each new cell contains its own nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles. _______ 14. In animal cells, centrioles, separate and take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus. _______ 15. Typically the shortest cycle in the cell division process. _______ 16. In plants, a structure known as the cell plate forms midway between the divided new cells. the nucleolus disappears, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. _______ 17. In plants, the cell plate gradually develops into a separating membrane. A cell wall then begins to appear in the cell plate formed from vesicles from the golgi. _______ 18. The DNA in chromatin (again) inside each new nucleus. _______ 19. The division of the cytoplasm itself. _______ 20. The condensed chromosomes become attached to fibers in the spindle at a point near the centromere of each chromatid.