* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Made of cisternae membrane sacs Sac of digestive enzymes that
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
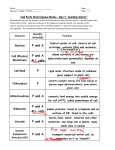
Made of cisternae membrane sacs “stacked like pancakes”; modifies, sorts, & packages molecules for export Sac of digestive enzymes that breaks down food, unwanted cells, or cell parts Plays a role in APOPTOSIS Storage space for food, waste, enzymes, & water that is larger in plant cells and smaller in animal cells. Membrane sacs inside chloroplasts that contain the enzymes for photosynthesis Contains the genetic material (DNA) & acts as the control center of the cell Molecule used by cells to store and transport energy Dark spot in the nucleus of a non-dividing cell where ribosomal RNA and proteins are made Powerhouse of the cell with its own DNA that burns glucose & stores energy as ATP for activities Found outside the cell membrane in plants and bacteria, this gives cell support and protection. Photosynthesizing organelle found in plants that contains chlorophyll in thylakoid sacs & its own DNA; Membrane system with ribosomes attached which modifies & transports molecules; cell’s “highway” Cell with a nuclear membrane and membranes around its organelles such as plants, animals, fungi, & protists Folded inner membrane in mitochondria which increases surface area for chemical reactions Phospholipid & protein bilayer that surrounds ALL cells and controls which molecules enter or leave LYSOSOMES GOLGI BODY (APPARATUS) THYLAKOIDS VACUOLE NUCLEOLUS NUCLEUS MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEOLUS CHLOROPLASTS CELL WALL EUKARYOTE ROUGH ER PLASMA (CELL) MEMBRANE CRISTAE Small structures (free or attached to Rough ER) which synthesize proteins Small internal structure in a cell which carries out a specific job Cell which has NO nucleus or organelles surrounded by membranes (Includes bacterial cells) Network of membranes WITHOUT RIBOSOMES which regulate calcium, make lipids, & break down toxins Molecule with a polar head and two hydrophobic tails which forms cell membranes Network of microtubules and microfilaments that give the cell shape, support, & help move cell parts Many, short; made of microtubules in 9+2 pattern; attached to outside of cells; help in movement Few, long; made of microtubules in 9 + 2 pattern; attached to the outside of cells which help move the cell DNA and proteins that are loosely coiled and spread out in the nucleus non-dividing cells Gel-like material containing organelles found between the nucleus and cell membrane DNA and proteins that are tightly packed up into rod shaped structures in dividing cells Membrane proteins with carbohydrates attached which help cells recognize “self” Log-like structures that appear in animal cells to guide the chromosomes apart in dividing cells Describes membranes which allow certain substances to pass through but keeps other out ORGANELLE RIBOSOMES SMOOTH ER PROKARYOTE CYTOSKELETON PHOSPHOLIPID FLAGELLA CYTOPLASM GLYCOPROTEIN SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE (Semi-permeable) CILIA CHROMATIN CHROMOSOMES CENTRIOLES TISSUES ORGAN SYSTEMS ATP NUCLEAR PORES NUCLEAR ENVELOPE ORGAN GLUCOSE AMINO ACID GLYCOPROTEIN PHOSPHOLIPID Openings in the nuclear membrane that allow molecules to pass in and out of the nucleus Group of similar CELLS that work together to carry out a specific job Membrane that surrounds the genetic material & controls what enters and leaves nucleus Groups of ORGANS that work together to carry out a specific function Group of different TISSUES that work together to carry out a specific function