* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Chromosome Gene Allele
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Sex-limited genes wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
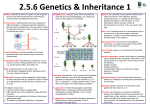
Genome All of the genetic information or hereditary material possessed by an organism; the entire genetic complement of an organism. Includes both nuclear & organelle genetic information. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Doubled stranded helix Sugar-phosphate backbone Complementary base pairing Adenine Thymine Guanine Cytosine Chromosome Discrete unit of the genome that carries many genes. Each chromosome consists of a long molecule of double-stranded DNA and proteins. Gene The functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. A gene is a sequence of DNA (A,C,G,T) that occupies a specific location on a chromosome. Genes encode the particular characteristics of individuals. Allele One of several alternative forms of a gene that occupies a given locus on a chromosome. Alleles can differ from one another in their phenotypic effects. At the molecular level, alleles differ from one another based on their nucleotide sequences, regardless of their effect on phenotype. Replicates itself – passes information from cell to cell Stores information (A, C, G, T) Controls the flow of information in organisms Transcription mRNA Translation protein Information is transmitted via the universal (nearly) genetic code Sex-linked traits Genes that are present only on the Xchromosome (no counterpart on the Y) Expression of trait depends on… e.g. in autosomes (not sex chromosomes) Traits are dominant when 1 copy of the gene is sufficient to express the trait. (1) sex of individual (2) dominant (or recessive) expression of trait ! " * Trait is expressed * * Sex-linked gene found only on the X-chromosome Traits are recessive when 2 copies of the gene are necessary to express the trait. Genes on the X-chromosome in females can be either homozygous or heterozygous Almost all genes on the X-chromosome in males are hemizygous (red-green color blindness, hemophilia A, e.g. of X-linked recessive traits) Trait is expressed Trait NOT expressed “carrier” Sex-influenced traits Genes are on autosomes, but trait expression varies between males & females (“male-pattern” baldness) Genotype Male Female B/B bald bald B/b bald not bald b/b not bald not bald John Adams (1735-1826) John Quincy Adams (1767-1848) Charles Francis Adams (1807-1886) Henry Adams (1838-1918) Sex-limited traits Genes are on autosomes, but trait expression is limited to either males or females (beard growth, milk production) Consequences of having genetic sex determination (1)! Dosage effects (2)! Sex-linked traits (3)! Degeneration of sex chromosomes Inversions SUPPRESS recombination… ACCTTG CATCGGTCTGAT AGGATTAG! “proto” X ACGTTG CATCGATCTGAT ACGATAAG! “proto” Y ACGTTG CATCGATCTGAT ACGATAAG! Inversion on “proto” Y ACGTTG TAGTCTAGCTAC ACGATAAG! ACGTTG TAGTCTAGCTAC ACGATAAG! “proto” Y (inversion) ACCTTG CATCGGTCTGAT AGGATTAG! “proto” X No recombination Why does SUPPRESSED recombination lead to degeneration?