* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
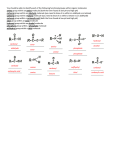
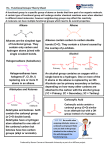
Rozaini Abdullah School of Bioprocess Eng UniMAP Week 10 Outline Carbonyl Condensation Micheal Reaction Aldol Claisen 1. Carbonyl Condensation Carbonyl compounds are both the electrophile and nucleophile in carbonyl condensation reactions Aldol Condensation Acetaldehyde reacts in basic solution (NaOEt, NaOH) with another molecule of acetaldehyde The b-hydroxy aldehyde product is aldol (aldehyde + alcohol) This is a general reaction of aldehydes and ketones General Condensations 5 Mechanism of Aldol Reactions Aldol reactions, like all carbonyl condensations, occur by nucleophilic addition of the enolate ion of the donor molecule to the carbonyl group of the acceptor molecule The addition intermediate is protonated to give an alcohol product Predicting Aldol Products The product will have an alcohol and a carbonyl in a 1,3 relationship (a beta-hydroxy carbonyl) 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and the carbon that was formerly the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule Mechanism of the Claisen Condensation Similar to aldol condensation: nucleophilic acyl substitution of an ester enolate ion on the carbonyl group of a second ester molecule If the starting ester has more than one acidic a hydrogen, the product b-keto ester has a doubly activated proton that can be abstracted by base Requires a full equivalent of base rather than a catalytic amount The deprotonation drives the reaction to the product Learning Check: Predict the product of Claisen condensation of ethyl propanoate Solution: Predict the product of Claisen condensation of ethyl propanoate Mixed Claisen Condensations Successful when one of the two esters acts as the electrophilic acceptor in reactions with other ester anions to give mixed b-keto esters 2.Conjugate Carbonyl Additions: The Michael Reaction Enolates can add as nucleophiles to ,b-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones to give the conjugate addition product Mechanism of the Michael Nucleophilic addition of a enolate ion donor to the b carbon of an ,bunsaturated carbonyl acceptor Learning Check: Make the following using a Michael Reaction: Solution: Make the following using a Michael Reaction: Learning Check: Which of the following statements explains why the following aldehyde will not undergo an aldol reaction with itself? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with the aldol reaction. Nucleophilic acyl substitution competes favorably with the aldol reaction. Solution: Which of the following statements explains why the following aldehyde will not undergo an aldol reaction with itself? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with the aldol reaction. Nucleophilic acyl substitution competes favorably with the aldol reaction. Learning Check: Predict the aldol reaction product of the following ketone. O NaOH Ethanol 1. 2. O 3. O OH O OH HO 4. 5. O OH O OH Solution: Predict the aldol reaction product of the following ketone. O NaOH Ethanol 1. 2. O 3. O OH O OH HO 4. 5. O OH O OH Learning Check: What type of reaction occurs in a Claisen condensation? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. electrophilic aromatic substitution nucleophilic addition hydrolysis nucleophilic acyl substitution decarboxylation Solution: What type of reaction occurs in a Claisen condensation? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. electrophilic aromatic substitution nucleophilic addition hydrolysis nucleophilic acyl substitution decarboxylation Learning Check: Select the correct Claisen condensation product for the following reaction. 1. 3. 2. 4. 5. Solution: Predict the outcome of the following reaction. 1. 2. 4. 3. 5.