* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 25R Cell Organelle Activity Biology “B”
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
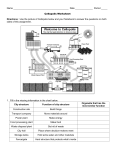
25R Cell Organelle Activity Biology “B” Name:___________________ Date: ___________ Period:________ Partner(s) Name(s) _______________________________________ Plant and animal cells have many organelles in common. Both have a nucleus (with specific numbers of chromosomes- depending on the organism), ribosomes, mitochondria, canals, Golgi apparatus, centrioles, and cell membrane. How you can tell whether a cell is a plant cell or an animal cell lies in the plant cell having a large water vacuole, a cell wall, and chloroplasts and the animal cell does not! All cells contain cytoplasm that is made up of mostly water and protein (making a “jello-like” material) that help hold organelles in place. Plant cells and animal cells differ in how they get sugar! Plant cells can make their OWN sugar using chloroplasts, by converting sunlight to sugar (they are called “producers”; that is they produce food). Animal cells must “eat” sugar to “get” it to their cells- so they are called “consumers” (take sugar in somehow). The key is- BOTH plant cells and animal cells MUST break down sugar to make energy packets (called ATP) that both types of cells MUST run on. Mitochondria (found in both plant and animal cells) help make ATP (mitochondria breaks down sugar products to make ATP) so cells can survive. ALL animal cells in some way, shape, or form break down plant sugar either directly (eat plants) or indirectly (eats animals). Plants can supply their own sugar so they do NOT have to “EAT”. YOU must turn this in for credit. Each person in the group must fill in this activity sheet and answer the questions at the end. (You can also use handout #23 pictures!) One activity sheet handed in per group!! Animal Cell- like a balloon Plant Cell- box-like structure not completely filled more rigid than animal cell Cell membrane Golgi Large water vacuole chloroplast mitochondria Cell wall nucleus canals Golgi Page 2 (Cont. #25R Cell activity lab) Both the animal and plant cell have a nucleus that contains genetic material (DNA). For our purposes, DNA and chromosomes are the same! The chromosomes will look something like this: See page 13 for other pictures. Chromosomes/DNA inside the nucleus control all the cell functions. This is why we call the nucleus the “brains” of the cell. It sends out messages to the rest of the celltelling the cell what to do. The important thing to understand is that the number of chromosomes strands has NOTHING to do with the complexity of an organism. For instance, human cells have 46 chromosomes (around 3 billion nucleotides) and a tobacco cell has 48 chromosomes. The number of chromosomes has NOTHING to with how smart an organism is or how successful it is in terms of survival! What matters to the organism is what information is stored in the chromosomes. That information is dependent on the sequence of the nucleotides in the strands of DNA! We actually find that many different organisms have the same number of chromosomes BUT since they are different organisms- they have different sequences of nucleotides in their DNA. Just look at the number of chromosomes for alga…148! We think of algae (sometimes known as pond scum) as being very primitive! Other parts of the cell have specific functions and this activity will reinforce those functions. We as multi-cellular organisms perform roughly the same functions as an individual cell. We breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Cells take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide as waste. Cells take in food, break it down and use the energy to keep the cell organized. We eat food and break it down to maintain our body- that is to stay organized! The canals inside the cell move cell material from one place to another. Our blood vessels move material from one place to another. Mitochondria help the cell by breaking down sugar products to energy packets called ATP. We used out stomach and intestine to help break down food and provide energy for all cells in our body. This activity requires that you use ALL the description of cell function found on page 3 of this handout. You are to: 1.) Cut out each description as carefully as you can. 2.) Match the description with the enlarged picture of the following pages and paste/tape them in place. The descriptions match the outlines near the figures of the organelles! (3 points each) 3.) Use the table on Page 18 to identify which organism you have (Pg.20) on the number of chromosomes in your nucleus (for extra credit). Page 3 (Cont. #25R Cell Organelle Activity Sheet Biology B) Answer the following questions on this handout ONLY! (2 points each) _____ 1.) What is the function of the largest organelle of the cell? a.) limits what goes into and out of the cell b.) helps give the cell shape c.) contains the cytoplasm and all the organelles in the cell d.) isolates the cell from its surroundings e.) all of the above are correct _____ 2.) What is the function of the cell organelle that looks like “flattened balloons”? a.) helps the cell move from place to place b.) helps cell make energy packets (ATP) c.) helps the cell make proteins d.) helps package the cellular material _____ 3.) What organelle found in both the plant cell and the animal cell helps make energy packets (ATP)? a.) ribosomes b.) nucleus c.) mitochondria d.) Golgi apparatus _____ 4.) What structure is made of cellulose and gives the plant cell shape while also resisting the pressure of a large water vacuole? a.) centrioles b.) cell wall c.) ribosomes d.) large nucleus _____ 5.) This organelle contains “grana”, is green, only found in plant cells, and helps the cell make sugar? a.) chloroplast b.) ribosome c.) Golgi apparatus d.) mitochondria _____ 6.) This organelle contains a lot of water, some salt, and some waste products that help give the plant shape. a.) Golgi apparatus b.) cell wall c.) ribosome d.) large water vacuole _____ 7.) This is the “brains” of the cell - contains genetic material (DNA) a.) ribosome b.) Golgi apparatus c.) canals d.) nucleus _____ 8.) This organelle is responsible for movement of material from one place in the cell to another. a.) nucleus b.) canals c.) ribosomes d.) cell membrane Page 4 (Cont. #25R Cell Organelle Activity Biology B) _____ 9.) This organelle helps the cell make proteins. a.) ribosomes b.) canals c.) cell wall d.) Golgi apparatus _____ 10.) This organism has 78 chromosomes in the nucleus. a.) chicken b.) radish c.) wheat d.) barley _____ 11.) Which organism is more complex and successful based on the number of chromosomes in the nucleus? a.) humans b.) earthworms c.) algae d.) dogs e.) none of these _____ 12.) Which organism has the same number of chromosomes as a human? a.) gorilla b.) hyena c.) mouse d.) musk deer _____ 13.) Which organism organisms are most likely to be closely related based on traits they have in common AND the number of chromosomes (mark all that apply)! a.) rabbit b.) human c.) orangutan d.) gorilla e.) chimpanzee Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Page 8 Page 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 This is the largest organelle the cell has. This organelle helps give a plant cell shape. This organelle is like the “skin” of a balloon. This organelle contains the cell’s cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, canal, ribosome, Golgi, apparatus, and centrioles. This organelle controls what goes into and out of the cell. This organelle isolates the cell from its surroundings. This organelle contains genetic material that controls the whole cell. This organelle is the “brains” of the cell. This organelle contains strands of chromosomes composed of DNA (nucleic acids stuck together). This organelle is where cell products are packaged. This organelle looks like flattened balloons. This organelle is also called the powerhouse of the cell. This organelle helps helps the cell make energy packets called ATP. This organelle is called “canals” or Endoplasmic Reticulum. This organelle helps move cell material from one place in the cell to another. These organelles are very small and cannot be seen with a light microscope. These organelles are found In the cytoplasm and help the cell make protein. These organelles can only be found in the plant cell and help the plant make sugar. These organelles are green and helps the plant cell perform Photosynthesis. This structure is found only in plant cells and contains cellulose. This structure helps give the plant cell rigidity and resists water pressure from large water vacuole. This organelle contains a lot of water, salt, sugar, and waste materials. This organelle provides water to help the plant Photosynthesis. This organelle helps Give the plant cell shape and when only partially filledcauses the plant to wilt. Plant Cell Animal Cell Page 21 (Cont. #26 Bio. B) Chromosome Numbers of Selected Animals and Plants (Diploid Number) Animal Camel Goat Guinea Pig Chinchilla Armadillo Opossum Porcupine Bat Porpoise Squirrel Shrew Alligator Salamander Chicken King Crab Drosophila (fruit fly) Mosquito Buffalo Chromosome Number 70 60 64 64 64 22 34 44 44 40 23(odd number/rare) 32 24 78 208 8 6 60 Plant Bean Barley Soybean Corn Pepper Lettuce Cowpea Mung bean Rye Petunia Pea Apple Tomato Rice Alfalfa Potato Chromosome Number 22 14 40 20 24 18 22 22 14 14 14 34 24 24 16 48 Lentil 14 Adder’s Tongue 1260-1400! Fern Human 46 Orange 18,27,36 Chimpanzee 48 Spruce tree 24 Dove 78 Onion 16 Earthworm 36 Spinach 10 Domestic Cat 38 Oak Tree 24 Rabbit 44 Foxglove (flower) 56 Muntjac(Musk deer) 46 Dandelion 24 Great Apes 48 Peanut 40 Domesticated Dog 78 Asparagus 30 Orangutan 48 Cotton 52 Cow 60 Carrot 18 Horse 64 Broccoli 18 Fox 36 Cucumber 14 Elephants 56 Daisy 18 Sheep 54 Willow tree 152 King Fisher (bird) 132 Redwood Tree 66 Ant (certain one) 1 Pine Tree 24 Those organisms that have more than one number – are often man-made plant crosses. Page 22 (cont. #25R Bio. B) What organism is this-based on the number of chromosomes? ________________________ Page 18 This is the largest organelle the cell has. This organelle helps give a plant cell shape. This organelle is like the “skin” of a balloon. This organelle contains the cell’s cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, canal, ribosome, Golgi, apparatus, and centrioles. This organelle controls what goes into and out of the cell. This organelle isolates the cell from its surroundings. Page 19 This organelle contains genetic material that controls the whole cell. This organelle is the “brains” of the cell. This organelle contains strands of chromosomes composed of DNA (nucleic acids stuck together). This organelle is where cell products are packaged. This organelle looks like flattened balloons. This organelle is also called the powerhouse of the cell. Page 20 This organelle helps helps the cell make energy packets called ATP. This organelle is called “canals” or Endoplasmic Reticulum. This organelle helps move cell material from one place in the cell to another. These organelles are very small and cannot be seen with a light microscope. These organelles are found In the cytoplasm and help the cell make protein. These organelles can only be found in the plant cell and help the plant make sugar. Page 21 These organelles are green and helps the plant cell perform Photosynthesis. This structure is found only in plant cells and contains cellulose. This structure helps give the plant cell rigidity and resists water pressure from large water vacuole. This organelle contains a lot of water, salt, sugar, and waste materials. This organelle provides water to help the plant Photosynthesis. This organelle helps Give the plant cell shape and when only partially filledcauses the plant to wilt. Page 22 Plant Cell Animal Cell Date: _______________________ Lesson Plan for Handout #25R Objective: TLWD ability to match the descriptions and the title of each organelle with its appropriate picture and be able to determine where chromosomes are located in the cell and be able to count the number of chromosomes and determine which organism has that number of chromosomes when given a list of organisms and the number of chromosomes each organism has when given handout #26. Content: Plant and animal cell structure, function, and organelle complement. Method: Puzzle pieces with picture representations of organelles...involves matching and answering several basic questions about data interpretation. NJCCCS: 5.3.12.A.1, 5.3.12.A.6. Homework: Complete Handout #25R