* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MS Word file
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
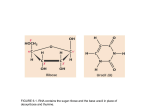
BSC 219 10/11/12 Transcription 13.1 RNA Consisting of a Single Strand of Ribonucleotides Participates in a Variety of Cellular Functions Primary structure Secondary structure Classes of RNA Ribosomal RNA – rRNA-part of ribosome Messenger RNA – mRNA-template of protein to be synthesized Transfer RNA – tRNA-transports amino acids to ribosome for translation Small nuclear RNAs – snRNAs Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins – snRNPs Small nuclear RNAs – snoRNAs Classes of RNA Small cytoplasmic RNAs – scRNAs MicroRNAs – miRNAs Small interfering RNAs – siRNAs Piwi-interacting RNAs – PiRNAs 13.2 Transcription Is the Synthesis of an RNA Molecule from a DNA Template The Template The transcribed strand: template strand Transcription will produce an RNA molecule that resembles the opposite strand or the nontemplate strand RNA polymerase moves along template strand in 3’-5’ direction and produces new RNA in 5’-3’ much as in DNA replication. The Template The transcription unit Promoter-initiates transcription RNA coding sequence-contains sequence that will be reflected in RNA molecule Terminator-halts transcription and releases RNA molecule Initiation The substrate for transcription: Ribonucleoside triphosphates – rNTPs added to the 3′ end of the RNA molecule rGTP, rCTP, rATP, and rUTP Initiation The transcription apparatus: Bacterial RNA polymerase: five subunits made up of the core enzyme: Two copies of α Single copy of β Single copy of β′ A stabilize enzyme: ω The sigma factor: binding to the promoter when transcription starts Initiation The substrate for transcription: Ribonucleoside triphosphates – rNTPs added to the 3′ end of the RNA molecule The transcription apparatus: Eukaryotic RNA polymerases Initiation Bacterial promoters: Consensus sequences: sequences that possess considerable similarity −10 consensus: 10 bp upstream of the start site Pribnow box: 5′ TATAAT 3′ 3′ ATATTA 5′ −35 consensus sequence: TTGACA Concept Check 2 The holoenzyme (core enzyme + sigma factor) The sigma factor alone The core enzyme alone mRNA Concept Check 2 The holoenzyme (core enzyme + sigma factor) The sigma factor alone The core enzyme alone mRNA Initiation Initial RNA synthesis: No primer is required. The location of the consensus sequence determines the position of the start site. Elongation RNA elongation is carried out by the action of RNA polymerase. Termination Rho-independent termination: hairpin structure formed by inverted repeats, followed by a string of uracils Rho-dependent termination: a hairpin slows down polymerase allowing a trailing protein called rho to catch up and dislodge the polymerase from the template 13.4 The Process of Eukaryotic Transcription Is Similar to Bacterial Transcription but Has Some Important Differences Transcription and Nucleosome Structure – Chromatin modification before transcription Promoters: Basal transcription apparatus Transcriptional activator proteins RNA polymerase II – mRNA synthesis Core promoter TATA box TATAAAA, −25 to −30 bp, binded by transcription factors Transcription and Nucleosome Structure – Chromatin modification before transcription Promoters: Regulatory promoter A variety of different consensus sequences may be found in the regulatory promoters. Main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is in assembly of complex structures at promoter in eukaryotes Transcription and Nucleosome Structure – Chromatin modification before transcription Enhancers: distant regions of DNA that increase transcription levels Bound by initiation complex proteins and loop around to interact with promoter region Polymerase I and polymerase III promoters Distinct from those of polymerase II May sometimes be downstream of transcription start site Initiation RNA polymerase II + transcription factors TATA binding protein Elongation Termination RNA polymerase I-terminated by protein that binds DNA downstream of termination sequence RNA polymerase II-terminated by complex mechanism involving RNA cleavage and Rat1 protein RNA polymerase III-terminates after long poly-U transcript. Concept Check 3 Only the core promoter has consensus sequences. The regulatory promoter is farther upstream from the gene. Transcription factors bind to the core promoter; transcriptional activator proteins bind to the regulatory promoters. Both b and c above Concept Check 3 Only the core promoter has consensus sequences. The regulatory promoter is farther upstream from the gene. Transcription factors bind to the core promoter; transcriptional activator proteins bind to the regulatory promoters. Both b and c above 13.5 Transcription in Archaea Is More Similar to Transcription in Eukaryotes than to Transcription in Eubacteria This suggests a closer relationship between archaea and eukaryotes.