* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
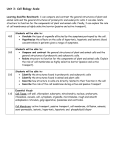
Name __________________________ Cells & Cell Transport Test Review (CP Bio) Notes on 3.1-3.5, Characteristics of Living Things notes, Bacteria Lab, Cheek/Onion Lab, Elodea Lab Activity, Diffusion Lab, Cell Project Cell Organelles & Functions 1. Complete the chart below for all of the organelles. Organelle Function Cell Membrane Contains digestive enzymes; waste management for the cell Control center of the cell. “Brain” of the cell. Chloroplast Cytoplasm Site of protein synthesis Roadway of the cell (lipids and carbohydrates). Breaks down toxins & poisons. Cytoskeleton Cell Wall Where energy is produced for the cell. The “powerhouse” of the cell. Golgi Body Controls what goes in and out of the nucleus Stores water for the cell. Is also the largest organelle in a plant cell. Rough ER Assist in cell division Nucleolus 1. Place a check mark in the correct boxes to indicate whether the cell part listed is found in plant cells, animal cells, or both: Cell Part Plant Cells Animal Cells Cell Wall Chloroplast Centrioles Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosome Nucleus Plasma membrane One large vacuole Ribosome Many small vacuoles 2. List the 4 structures that are common to all cells (both prokaryotic and eukaryotic)? What is a structural difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? 3. Why are prokaryotic cells so much smaller than eukaryotic cells? 4. List the 3 parts of the cell theory. 5. List examples in cells & the human body of when we see increased surface area for more efficient functioning. 6. List the 5 steps involved in exporting membrane & secretory proteins from the Rough ER out of the cell membrane. 7. Describe the structure of the cell membrane. Cell Transport 1. Explain passive transport. Give 3 types of it, explaining what each accomplishes. Passive Transport is: The three types and their definitions are: 1. 2. 3. 2. Explain active transport. Give 3 types of it, explaining what each accomplishes along with examples of one of these types. Active transport is: The three types of active transport and their definitions are: 1. 2. 3. 3. What two forms of transport can endocytosis be broken into? What are their definitions? 1. 2. 3. Draw a red blood cell in an isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solution. Draw dots to show the solute concentration and draw arrows to show which way the water would move. (Osmosis) Isotonic Hypertonic Hypotonic 4. What did the setup of the “Diffusion through a Membrane Lab” look like before and after 10 minutes? What happened that let you be certain that diffusion took place? 5. How do you know the dialysis tubing was semi-permeable? Miscellaneous: 1. The cell membrane contains both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. Define these terms and state which parts of the phospholipid bilayer apply to each term. 2. What characteristics must something have to be considered living?