* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Unit 3—Cell Biology-- Study Guide
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
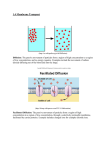
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
1 Biology Unit 3—Cell Biology-- Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chapters 2 & 7 Concepts 2-2 Concepts 2-3 Concepts 2-4 Concepts 7-1, 7-2 Concepts 7.3 pH Molecules of Life Enzymes Cell Structure & Function Homeostasis & Cell Transport Key Terms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Enzyme Protein Polysaccharide Nucleic Acid Lipids Prokaryote Eukaryote Phospholipid Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus (complex) Cytoskeleton Cell Wall Active transport 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Selectively (semi) permeable Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic Passive transport Diffusion Osmosis Plasmolysis Facilitated diffusion Exocytosis Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Recommended Work For Chapters 2 & 7: Chapter 2 Section 2 #2, 4 Section 3 #1, 2, 3, 4 Chapter Review # 8, 9, 10, 18, 19, 24, 25 Chapter 7 Section 1 #1, 2, 4 Section 2 #1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Section 3 #1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Section 4 #1, 2, 3, 4 Chapter Review #1-10, 12-25 1 2 Biology Unit 3—Cell Biology—Packet Life’s little compartments: Types of cells and how they work After the last unit, this one may be a little refreshing, since almost all you need to know about this unit can be summarized in a few tables and figures. This unit is about cells Define cell:______________________________________________________________ and parts of cells, and its builds upon the information presented in the last unit. While studying this unit, note that in cells, different types of reaction and products are produced in a compartmentalized world. One way the living world stays compartmentalized is with membranes. Define:_______ ________________________________________________________________________ Cells and cell organelles Define organelle:____________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ are surrounded by a membrane, a selectively permeable Define:___________________ ________________________________________________________________________ barrier that segregates cell contents from the outside world. In this unit you’ll learn the basic components of the cell. In the laboratory exercise, you’ll learn how the membrane allows transport of certain materials between compartments. Cells and cell organelles come in many different sizes to form simple or complex organisms. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes There are two main types of cells—prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Compare and contrast these two types of cells. Compare: Contrast: 2 3 Biology Unit 3—Cell Biology—Packet Structure and Function of the Cell The plasma membrane separates internal metabolic events from the external environment and controls the movement of materials into and out of cell. The plasma membrane is a double phospholipid membrane (lipid bilayer) with the polar hydrophilic heads forming the two outer faces and the nonpolar hydrophobic tails pointing toward the inside of the membrane. Draw and label the plasma membrane with the following parts: polysaccharide chain, phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol, transport protein, hydrophobic tails, hydrophilic heads. Describe why the plasma membrane is described as a Fluid Mosaic Model. Describe the following features of the plasma membrane: 1. Phospholipid membrane 2. Proteins a. Channel protein 3. Cholesterol 3 4 Biology Unit 3—Cell Biology—Packet Organelles are bodies within the cytoplasm that serve to physically separate the various metabolic reactions that occur within the cell. Complete the following chart and the worksheet at the end of the packet. Know how the label a diagram of an animal cell and plant cell. Know the function of each organelle. Prokaryotes Bacterial Eukar yotes Plant cells Animal cells Size Structure Cytoplasm Function or Properties --Yes or No-- --Yes or No-- --Yes or No-- Nucleus Plasma membrane Cell wall Chromosome Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Lysosomes Vacuoles Mitochondria 4 5 Biology Unit 3—Cell Biology—Packet Movement of Substances Various terms are used to describe the movement of substances between cells and into and out of a cell. Describe the following terms that involve membranes that are selectively permeable. 1. Passive transport 2. Simple diffusion 3. Osmosis 4. Hypertonic 5. Hypotonic 6. Isotonic 7. Plasmolysis 8. Facilitated diffusion 9. Active transport 5 6 Biology Unit 3—Cell Biology—Packet 10. Exocytosis 11. Endocytosis (phagocytosis, pinocytosis) 12. Receptor-mediated endocytosis Complete the following table: TYPES OF TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE Type of Transport Requires Concentration Gradient Energy? Gradient (Yes or No) (Down, Up, or N/A) Passive (Diffusion) Osmosis (Diffusion of H2O) Facilitated Diffusion (via carrier protein) Active Transport (ATP mediated) Exocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Receptor-mediated Endocytosis 6