* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Honors Final Review
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
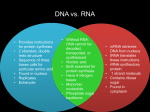
Department Biology Final Review 10/11 Unit: 1 1. Describe the steps of the scientific method. 2. In an experiment, what is the dependent variable? What is the independent variable? 3. What is a hypothesis? How is a hypothesis written? Write a possible hypothesis about how you will do on this exam… 4. Explain the difference between a control group and an experimental group. Why must every experiment have a control group? 5. Define biotic and abiotic. Unit: 2 1. What is an organic compound? What are the four organic compounds used in living things? 2. What is an enzyme? How does it effect a chemical reaction? Unit: 3 1. When looking at an organism (on a slide) through a microscope the organism should be placed in the ____________ of the field of view. 2. List the 3 parts to the cell theory. 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4. Complete the following chart: Organelle Function Eukaryotic/Prokaryotic/ Both Plant/Animal/Both Nucleus Nuclear membrane Nucleolus Rough ER Smooth ER Golgi body (apparatus) Lysosome Mitochondria Chloroplast Vacuole Ribosome Cell membrane Cell wall Cytoplasm Unit: 4 1. Compare and contrast passive and active transport. 1 2. If an animal cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, which way does the water move? In a hypotonic solution? In an isotonic solution? 3. What organelle regulates what gets into the cell? 4. Describe exocytosis and endocytosis. Why are these processes important to a cell? Unit: 5 1. What types of organisms use photosynthesis? 2. Where does photosynthesis occur? 3. What is the cell’s energy currency? 4. Why is photosynthesis important to all life on Earth? 5. What is cellular respiration? What organisms use it to get energy? 6. What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? 7. What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration? 8. Describe alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation. What types of cells use these processes? What element is not present when these processes occur? Unit: 6: 1. What is a somatic cell? A gamete? 2. Define the following: gene, chromosome, chromatid, homologous chromosomes, haploid, diploid. How do these terms relate to one another? 3. What is mitosis? What types of cells are produced by mitosis? 4. When normal control of the cell cycle fails, __________ may develop. 5. What is a mutation? What are the 4 types mutations? 6. What kinds of cells are produced by meiosis? How many are produced? 7. What is crossing over and when can it occur? 8. What is gametogenesis? (hint: spermatogenesis/oogenesis? Where does it occur?) 9. Describe asexual reproduction and the different types. 10. Describe sexual reproduction. 11. What is produced by asexual reproduction? 12. Which type of reproduction creates the most opportunity for genetic diversity? Why is this important to life? 13. If a body cell has 52 chromosomes, how many chromosomes are in the haploid gamete? Unit: 7: 1. What is DNA? What is the purpose of DNA? What does DNA stand for? 2. Why does every cell contain DNA? Where is DNA located? 3. The building blocks of DNA are called ________________, which have 3 parts: _________________________, ________________________, _______________________________. 4. Draw a building block of DNA and label the 3 parts. 2 5. What is replication and when does it happen? Why is this process important? 6. If a DNA strand, AATCTGG, is replicated, what would the complimentary strand be? 7. What is the function of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA? 8. Why does DNA make mRNA? What is this process called? Where does it happen? 9. Describe the steps of making mRNA from DNA. 10. Compare and contrast RNA and DNA. 11. What are the building blocks of proteins? How many different types are there? 12. How are proteins formed? What is this process called? Where does the process occur? 13. If the following strand of DNA is used to make mRNA, what codons will be found on the mRNA? DNA: TTTACGCGGT 14. If the following codons were found on mRNA, what would the anticodons on tRNA be? mRNA: CAG-AAA-UAU-UUU 15. What amino acids would be added together based on the codons found on this strand of mRNA? mRNA: AUG-UAU-UUU-CCG-AUC Unit: 8: 1. Who was the father of genetics? 2. Describe his experiments with the garden pea. What did he discover? 3. Describe the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment. Why are these important to genetic variation? 4. Black eyes (B) are dominant to red eyes (b) in rats. If a heterozygous rat and a rat with red eyes mate, what is the probability that the offspring will have red eyes? 5. If tall is dominant (T) to short (t) in pea plants, what would the genotype be if a plant’s phenotype was short? 6. How is meiosis related to genetics? 7. Define the following terms: homozygous, heterozygous, phenotypes, genotypes, alleles, dominant, recessive, codominance, incomplete dominace, genetics and heredity. Evolution 1. Define the following terms: evolution, analogous structures, homologous structures, vestigial structures, fossils. 2. Who is given credit for developing the theory of evolution? What did his theory say? 3. What evidence supports the theory of evolution? 4. Describe the process of natural selection. How does this process affect evolution? 3 Population and Ecology 5. Define the following terms: population, species, ecosystem, ecology, community, abiotic factors, biotic factors, density dependant factor, density independent factors, exponential growth, carrying capacity, habitat, niche. 6. List examples of biotic and abiotic factors. How do these factors affect a population? 7. Describe the difference between density dependent and density independent factors. Give some examples of each. 8. Draw and label the various parts of a population growth curve. What happens if the population goes above the carrying capacity? 9. What is succession? Describe secondary succession. 10. How is a species habitat different from its niche? 11. What is a food chain? A food web? A food pyramid? Where would herbivores and carnivores be found in each? 12. Describe the function of a primary producer in an ecosystem? 13. What does an omnivore eat? A carnivore? An herbivore? 14. Describe the following symbiotic relationships: mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Give examples of each. 15. How are humans affecting the environment? Biomes 16. What are the terrestrial biomes? Give the characteristics of each of those biomes. 17. Which biome has the most diversity, but the most infertile soil? 18. Where is permafrost found? 4 19. What biome has grazing herds? Classification 20. What is taxonomy? 21. What is binomial nomenclature? Who created it? 22. List the levels of classification for the largest to smallest. (Hint: Domain is the largest.) 23. What are the six kingdoms? (fill out the chart below) Kingdom uni or multi cellular hetero or auto troph examples importance 24. Explain the importance of a flower and a fruit for plants. What are the parts of a flower? What is each part’s function? 25. What is an invertebrate? A vertebrate? 26. How are reptiles different than amphibians? 5