* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
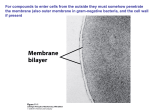
NAME ____________________________ DATE ____________ PERIOD _____ CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION REVIEW MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins The nucleus includes all of the following EXCEPT ____________________ A. cytoplasm B. nuclear envelope C. DNA D. nucleolus E. chromatin Cells like muscle cells which require lots of energy would probably have many ____________________. A. nuclei B. flagella C. mitochondria D. lysosomes Viruses, bacteria, and old organelles that a cell wants to get rid of are broken down in ______________ A. ribosomes B. mitochondria C. rough ER D. lysosomes Mitochondria store the energy released when they burn glucose as ______________________. A. DNA B. ATP C. SER D. RNA The structures that synthesize proteins in cells are the ____________________. A. ribosomes B. Golgi apparatus C. lysosomes D. vacuoles 1 The folded inner membrane in mitochondria which increases the surface area for chemical reactions to take place is called the ________________. A. thylakoids B. centrioles C. chromatin D. cristae The dark spot seen in the nucleus in non-dividing cells where RNA for ribosomes is made is called the ______________________ A. cristae B. nucleolus C. plastids D. cytosol The cells organelles that are surrounded by DOUBLE MEMBRANES and contain their OWN DNA are the _________________ A. nucleus, ER, and lysosomes B. nucleus, vacuoles, and chloroplasts C. nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria D. ER, Golgi bodies, and vacuoles One difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes is that _____________________ A. prokaryotes are surrounded by a cell membrane and eukaryotes are not B. prokaryotes have a nucleus and eukaryotes don’t C. eukaryotes have DNA and prokaryotes don’t D. eukaryotes have membranes around their nucleus and organelles and prokaryotes don’t Vacuoles are _______________ in plant cells than in animal cells. A. smaller B. larger Cell membranes form because the hydrophobic tails on phospholipids try to ________ water. A. be near B. stay away from * * * * * * * * * * * * * Name two organelles found in plant cells that are NOT seen in animal cells. ____________________________ ____________________________ Tell one way you can tell this cell is NOT A PLANT CELL. ___________________________________ Tell one way you can tell this cell is NOT A BACTERIA. _________________________________ 2 TELL TWO (2) WAYS EACH OF THE FOLLOWING ARE DIFFERENT? CHROMATIN CHROMOSOME CILIA FLAGELLA * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * CHARACTERISTICS OF CELLS TRAIT Prokaryote or Eukaryote? PLANT CELL ANIMAL CELL Presence of Nuclear Membrane? Presence of Cell Wall? Vacuoles --- Small, Large, None? With or without Centrioles? Chloroplasts? Mitochondria? * * * * * * * * * * CELL THEORY 1. All living things are ____________________________. * 2. Cells are the basic unit of _______________ & ______________ in an organism (= basic unit of life) 3. Cells come from the reproduction of __________________________ * * * * * * * * * * * * English scientists who first saw “little boxes” in CORK that he named cells ___________________ Dutch microscope maker who was the first to observe LIVING cells ____________________________ 3 * * * * * * _____________ CELL * * * * * * * * * * * * _____________ CELL ____________ CELL * * * * * * * NUMBER AND NAME THESE LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION IN THE CORRECT ORDER FROM SIMPLEST TO MOST COMPLEX. ____ _______________ _____ ______________ _____ _______________ _____ _______________ _____ _______________ _____ _______________ * 4 * _____ _______________ _____ _______________ _____ ______________ * * * * * * * * * * * * * THE WORD BEGINS WITH? 1. Small structure in a cell that performs a specific function is the _O_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 2. Sac of digestive enzymes = _L_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 3. _R_ __ __ __ __ ER is covered by ribosomes and sends its modified proteins to the Golgi apparatus. 4. The _C_ __ __ __ _W_ __ __ __ is found outside the cell membrane in plants and bacteria and provides support and protection. 5. An organism like a green plant that can make its own food = _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 6. These sausage shaped organelles burn glucose and store the energy as ATP = _M_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 7. The molecule used by cells to store genetic information = __ __ __ 8. An organism with a nuclear membrane and organelles surrounded by membranes = _E_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 9. The _N_ __ __ __ __ __ __ is surrounded by a double membrane, contains the cells DNA, and acts as the control center. 10. One or two long, hair-like structures called _F_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ extend from the surface of cells and help move the cell. 11. The _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ is the gel-like material plus the cell’s organelles. 12. The function of ribosomes is to make _P_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. ER is an abbreviation for _E_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ _R_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 5 14. __ __ __ __ __ __ ER does NOT have ribosomes attached. 15. The thylakoid sacs found inside a _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are where photosynthesis happens in plant cells. 16. A _G_ __ __ __ __ _B_ __ __ __ looks like a stack of pancakes and packages molecules for transport out of the cell. 17. Space for storing food, water, enzymes, or waste = _V_ __ __ __ __ __ __ 18. An organism (like you) that CAN’T make its own food and gets it energy by eating other organisms = _H_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 19. A _P_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ is an organism like a bacteria with NO NUCLEAR MEMBRANE and NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES. 20. The _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ is made of microtubules and microfilaments in the cytoplasm that provide support and give the cell its shape. 21. _C_ __ __ __ __ are many short hair-like structures on the surface of a cell that help move the cell or move substances past the cell. 22. _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are log-like structures that appear during cell division in animal cells and pull the chromosomes apart. * * * * * * * * * * * * * OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) _________________ __________________ _________________ __________tonic means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. __________ tonic means there is a LOWER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. __________tonic means there is the SAME concentration of solute molecules outside the cell as inside. The SWELLING AND BURSTING of animal cells happens when a cell is placed in a _________tonic solution. 6 The SHRINKING of plant cells when water leaves so the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall happens when a plant cell is placed into __________tonic solution. Cells stay the same size when placed in an ________tonic solution because the amount of water leaving the cell is the same and the amount of water entering. * * * * * * * * * * * * MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle the answer(s) that best completes the sentence. The substance that dissolves to make a solution is called the ___________________ A. diffuser B. solvent C. solute D. concentrate During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system, the system has reached __________________. A. maximum concentration B. homeostasis C. osmotic pressure D. equilibrium The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called ________________. A. active transport B. facilitated diffusion C. osmosis D. phagocytosis Phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and exocytosis are all kinds of _______________ transport. A. active B. passive ________________ transport requires energy from ATP to move substances across membranes. A. Passive B. Active 7 * White blood cells engulf, digest, and destroy invading bacteria using __________________. A. Facilitated diffusion B. pinocytosis C. phagocytosis D. osmosis Endocytosis that brings in small dissolved molecules (solutes) and fluids is called ___________________. A. pinocytosis B. phagocytosis C. facilitated diffusion D. osmosis Placing an animal cell in a hypotonic solution will cause water to ______________________. A. move into the cell B. move out of the cell When molecules move DOWN the concentration gradient it means they are moving from ______________ A. an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration B. an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration * * * * * * * Complete the transport terms. * * * * * * 1. _A_ __ __ is the molecule that provides the energy for active transport. 2. _D_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __moves oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration across membranes. 3. Water moves across membranes by _O_ __ __ __ __ __ __. 4. A small membrane sac used to transport substances during exocytosis & endocytosis = _V_ __ __ __ __ __ __ 5. _P_ __ __ __ __ __ __ transport does NOT REQUIRE energy. 6. During _F_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ diffusion carrier proteins grab glucose molecules, change shape, and flip to the other side of the membrane, like a revolving door. 7. A cell placed in an _I_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ solution neither swells or shrinks because the concentration of molecules outside the cell is the same as inside. 8. A solution in which there is a HIGHER concentration of molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside = _H_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 9.Pinocytosis, phagocytosis, and Na+-K+ pumps are all kinds of _A_ __ __ __ __ __ transport because they use energy to move substances across membranes. 10. A solution in which the concentration of molecules outside the cell is LOWER than inside = _H_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 8