* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry Review
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
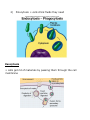
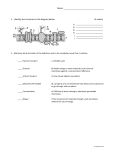
Cell Processes – Day 1 Homeostasis = ability or tendency to maintain internal balance AKA balance = equilibrium Why important? - Without this balance cells will die Cell Membrane - AKA 1) Fluid Mosaic Model 2) Plasma Membrane 3) Phospholipid Bilayer - Composed of a lipid bi-layer w/ embedded proteins - Functions: 1) Regulates what enters & exits cells 2) Provides protection & support - Cell Membrane is selectively permeable Types of Membranes 1) 2) 3) Permeable = anything can cross Impermeable = nothing can cross Selectively Permeable = some things can cross but not others Definitions Solution = mixture of 2 or more substances Concentration = amount of substance you are dissolving in a solution Equilibrium = concentration on both sides of a membrane is equal Diffusion = movement of particles form area of higher concentration to area of lower concentration - Does NOT require energy Facilitated Diffusion = moving larger particles with help from proteins in membrane Cell Processes – Day 2 Osmosis = diffusion of water 3 Types Osmosis 1) Hypertonic = greater solution outside cell than inside 2) Hypotonic = lower concentration inside cell than inside 3) Isotonic = concentration outside cell equals inside cell Osmotic Pressure = pressure exerted on a cell membrane due to different concentrations on the inside and outside of cell Cell Processes – Day 3 Active Transport = movement of molecules from low concentration to high concentration (against concentration gradient) - REQUIRES energy Endocytosis = cells take in materials they need 2 Types of Endosytosis: 1) Phagocytosis = cells eat materials they need 2) Pinocytosis = cells drink fluids they need Exocytosis = cells get rid of materials by passing them through the cell membrane Feedback Mechanism = system responds positively in the same direction or negatively in the opposite direction Positive Feedback = feedback results in growth of signal - Example: If you eat a McDouble at McDonalds, a hormone is released to your brain to signal satiation. You will feel the same “happiness” each time you eat the hamburger. Negative Feedback = feedback in which system responds in opposite direction - Example: If your blood sugar levels at continuously high it may result in diabetes.