* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Expression - Phillips Scientific Methods
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
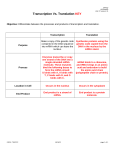
NAME: ____________________________ PERIOD: _____ DATE: _______________ General Questions – Gene Expression 1. What is the purpose of replication? 2. What is the purpose of transcription? 3. What is the purpose of translation? 4. Where does replication occur in eukaryotic cells? 5. Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells? 6. Where does post-transcriptional processing occur in eukaryotic cells? 7. Where does translation occur in eukaryotic cells? 8. Circle all that apply a) DNA Polymerase is used in Replication Transcription Translation b) RNA Polymerase is used in Replication Transcription Translation c) Pyrophosphate powers Replication Transcription Translation d) ATP & GTP powers Replication Transcription Translation 9. Describe the role of each of the enzymes discussed in Replication 10. Describe 3 ways that the RNA that leaves the nucleus differs from a primary transcript? 11. Define each of the following, and explain what type of point mutation could cause each of these mutations. a) Silent mutation b) Missense mutation c) Nonsense mutation d) Frameshift mutation NAME: ____________________________ PERIOD: _____ DATE: _____________ You are given the following DNA in order to be made into a protein. 5’ end ATG TCT ATA AGC AAA CGA CAA GGC GGT TAA 3’ end 3’ end TAC AGA TAT TCG TTT GCT GTT CCG CCA ATT 5’ end 1. Write out the sequence of BOTH products of replication. What do you notice about these products? 2. Which strand is the coding strand and which is the non-coding strand in the DNA molecule above? (Label the strands on the diagram above) 3. Write out the mRNA that would be transcribed from the coding strand above, be sure to specify both the 5’ and 3’ ends 4. Write out the sequence of tRNA anti-codons that is complementary to the mRNA sequence above: 5. Translate the mRNA into an amino acid chain using the 3-base codons on the mRNA molecule you wrote in the space above. You may need to use codon chart on pp. 330 NAME: ____________________________ PERIOD: _____ DATE: _______________ Comparison Chart Replication Where? What is used as the template? What is the new strand composed of? What is used to synthesize the new strand? Which Nucleotides are involved? Where does the finished product go? What happens in Post-Processing? Transcription Translation NAME: ____________________________ PERIOD: _____ DATE: _______________ Gene Expression Arrange the following by their occurrence in protein synthesis or gene expression. _____ A release factor binds to the “A” site of the ribosome. _____ The ribosome falls off the mRNA. _____ RNA Polymerase binds to the DNA strand to complete the transcription initiation complex. _____ The ribosome reaches UAA, UAG or UGA. _____ snRNPs attach to the beginning and ending sequences of introns. _____ Using GTP for power, the tRNA in the “A” site moves to the “P” site. _____ A guanine cap and a 50-250 nucleotide Poly–A tail are added to the mRNA. _____ The tRNA of the “P” site moves to the “E” site and then leaves the ribosome. _____ The small subunit of the ribosome binds to the leader segment of mRNA and a methionine tRNA. _____ GTP is used to attach the large subunit of the ribosome to the mRNA initiation complex. _____ The next tRNA matches its anti-codon to the codon of the “A” site. _____ Spliceosome adheres to snRNPs and excises introns while sealing exons into a continuous strand of mRNA. _____ Two GTPs are used to transfer the amino acid onto the polypeptide in the “A” site. _____ RNA Polymerase pulls the double helix strands apart 10-20 base pairs at a time to reveal the nucleotide sequence of the template strand. _____ RNA nucleotides are added to the 3’ end of the growing strand of mRNA at the rate of ~60 per second. _____ mRNA leaves the nucleus through a nuclear pore. _____ The ribosome continues to move from the 5’ end to the 3’ end, adding amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. _____ The termination sequence is transcribed and the RNA Polymerase falls off.