* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Quiz
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
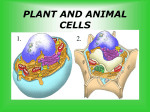
Name: ______________________ Class Period: ________________ Date: ______________________ Cell Quiz Directions: Write the correct answer in the line in front of the question. ______1. Life is organized in a hierarchical fashion. Which of the following sequences illustrates that hierarchy as it goes upward? a. molecule, cell, organ, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem b. ecosystem, molecule, cell, organism, organ system, organ, community c. cell, molecule, organ system, organ, population, organism, ecosystem, community d. organism, organ system, population, organ, community, cell ecosystem, molecule ______2. Select the smallest level of organization among the following: a. organ b. organ system c. organism d. tissue ______ 3._______ is the main purpose of ribosomes? a. Transporting proteins b. Protection of the cell c. Protein manufacture d. Energy production ______ 4. A ______ is the storage compartment of a cell. a. Cytoplasm b. Vacuole c. Cell Wall d. Lysosome ______ 5. ______ is the thick, clear fluid that holds the organelles in place. a. Cytoplasm b. Vacuole c. Cell Wall d. Cell Membrane ______6. A ______ is where an animal cell digests food. a. Cytoplasm b. Vacuole c. Cell Wall d. Lysosome ______7. The ______ is the outer boundary of an animal cell. a. Cytoplasm b. Organelle c. Cell Wall d. Cell Membrane ______8. A _______ is the hard, protective, nonliving outer boundary of a plant cell. a. Cell membrane b. Vacuole c. Cell wall d. Chlorophyll ______9. The ________________ is the energy processor in cells. a. Nucleus b. Vacuole c. Cell Wall d. Mitochondrion 11. Label the following cell: Name: ______________________ Class Period: ________________ Date: ______________________ ______8. What passes through the cell membrane during osmosis? a. food b. water c. proteins d. salt ______9. The cell membrane allows some substances to pass through but not all substances. What is this called? a. diffusion b. osmosis c. semi-permeable d. endocytosis ______10. When molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, we call this . a. endocytosis b. osmosis c. semi-permeable d. diffusion ______17. Which cellular structure is NOT found both in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? a. plasma membrane b. mitochondria c. genetic material (DNA) d. cell wall e. ribosomes Match the following word with the definition. a. prokaryotic b. photosynthesis c. unicellular d. eukaryotic e. multicellular ______14. Robert Hooke was . . . a. the first to see a cell in a slice of cork and name it. b. the first to say that plants are multicellular c. the first to say that the whole plant was made of cells. d. the founder of the cell theory ______15. The cell theory states that (circle all that apply). a. Living cells can come from nonliving cells. ______18. The process in green plants and certain other organisms by which carbohydrates are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water using light as an energy source. ______19. Any cellular organism that has a membrane bound nucleus, organelles in the cytoplasm, and has its genetic material in the nucleus. b. All living things are made of one or more cells c. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. d. All cells are produced by the dividing of preexisting cells. ______16. One of the main differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells is the... a. lack of chlorophyll in eukaryotes b. larger size of prokaryotes c. presence of a cell wall in prokaryotes d. presence of a nucleus in eukaryotes ______20. composed of one cell.