* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Biology
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
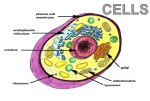
Cell Biology Part 2 Cytoskeleton Network of protein fibers and in the cytoplasm. Functions • Cell structure and shape. • Cell movement. • Cell division - helps build cell walls and move the chromosomes apart. Components of the Cytoskeleton Organized in deceasing diameter • Microtubules • Microfilaments • Intermediate Filaments Microtubules • Structure - small hollow tubes made of the protein “tubulin”. • Size - 25 nm outer diameter with a 15 nm inner diameter. Can be 200 nm to 25 mm in length. Microtubules • Found in the “spindle” apparatus (during cell division), cilia, flagella, basal bodies and centrioles. Functions • Maintenance of cell shape. • Hold organelles in place. Microfilaments • 5 to 7 nm in diameter. • Structure – made up of the protein “actin” Functions • Muscle contractions. • Cytoplasmic streaming. • Pseudopodia (amoeboid movement) found in amoebae and phagocytes (white blood cells). • Cleavage furrow formation. • Maintenance and changes in cell shape. Microfilaments are stained green. Cilia and Flagella Classified by their lengths and numbers • Cilia - short, but numerous. • Flagella - long, but few. • Function - to move cells or to sweep materials past a cell. Cilia and Flagella • Structure - 9+2 arrangement of microtubules, covered by a plasma membrane (different in bacteria) • Made of contractile proteins • Uses ATP Centrioles and Basal Bodies act as “microtubule organizing centers” or MTOC’s Centrioles • Usually one pair per cell, located close to the nucleus. • Found in animal cells only. • 9 sets of triplet microtubules. • Help in cell division. Basal Bodies • Same structure as a centriole. • Found at the base of the cilia and flagella. Plant Cells Plant Cell Cell Wall • Nonliving jacket that surrounds some cells. • Found in: –Plants –Prokaryotes –Fungi –Some Protists Plant Cell Walls • All plant cells have a Primary Cell Wall. • Some cells will develop a Secondary Cell Wall. Cell Walls • Plant cell walls are made of cellulose ( a polysaccharide made of b-glucose). • Fungi cell walls are made of chitin (a polysaccharide) • Function as the cell's exoskeleton for support and protection. Middle Lamella • Thin layer rich in pectin (used to make jelly) found between adjacent plant cells. • Glues cells together. Vacuoles and Vesicles Fluid-filled, membrane-bound bodies 5 Types of Vacuoles and Vesicles • Transport vesicles • Food vacuoles • Storage vacuoles • Central vacuoles • Contractile vacuoles The function of the vacuole depends on the organism. In Protists (single-cell organisms) • “Food” vacuoles store newly ingested food until the lysosomes can digest it. • “Contractile” vacuoles pump out excess water. Contractile Vacuole Contractile Vacuole Food Vacuoles Central Water Vacuole • Large single vacuole when mature making up to 90% of the cell's volume. Function of Central Water Vacuole • Water regulation. • Storage of ions. • Storage of hydrophilic pigments. (e.g. red and blues in flower petals). Other vacuoles and vesicles • Storage vacuoles in plants store starch, pigments and toxic substances (such as nicotine) • Transport vesicles move materials from one organelle to another, or from organelle to the plasma membrane. (“exocytic vesicles” move materials to the plasma membrane for export, “endocytic vesicles” transport materials from outside the cell to the plasma membrane to be imported) Chloroplasts • Contain DNA. • Can reproduce themselves. • Often contain starch. • May have been independent cells at one time. Function of Chloroplasts • Photosynthesis - chloroplasts use of light energy to make food. (sugars) • Contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Chloroplasts Enzymes in a crystal Chromoplasts store plant pigments such as chlorophyll, carotene. • Found in plants only. • Classified (named) by color example: Chloro means green, therefore a chloroplast is a green plastid that stores chlorophyll • Leuco means white, therefore Leucoplasts (AKA Amyloplasts) are white plastids that store starch. Comparing Plant Cells and Animal Cells Plant Cells Animal Cells Have cell walls, chloroplasts, and central water vacuoles…animal cells do not!! Have lysosomes and centrioles…. Plant cells do not!!