* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microworlds Study Guide
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
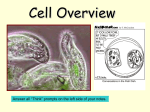
Microworlds Study Guide Anton Leeuwenhoek He was the _________ person to make and use over _________________________. Leeuwenhoek lived in the 1600’s in the _________________________. Most of his microscopes were very __________________, just 1”x2”. He was the first person to ever see _____________________________ plants and animals. He discovered ___________________ when he scraped ______________ from his teeth. He also discovered that mammals have ______________________ while birds and fish have ______________________________. Only 9 of Leeuwenhoek’s 240 microscopes remain today. Robert Hooke Robert Hooke lived in the _____________ in ______________________ One of the differences between Leeuwenhoek and Hooke was that Hooke ___________ what he saw under the microscope. Hooke invented the Barometer. Meteorologists use them to detect air pressure. Hooke also worked to ___________ microscopes. He learned that making the lenses MORE ______________ makes them more powerful. Volvox Commonly found in ____________________. It is part of a group of organisms called __________________ __________________. A Volvox doesn’t have _____________, ________________, or ______________, but they are like green plants because they make their own food. This process is called ________________________________. They live in a colony of ______________ to ___________________ similar cells. The Volvox forms a _______________. They live in a ___________________ substance. Each cell has two tails called ________________. These tails are what move the Volvox through the water. It rolls like a _________________. There are _______________ ___________________ that split from the parent colony when they are big enough to begin their own Volvox colony. Blepharisma Commonly found in ___________________. It is a _____________ __________________ pear shaped organism. It has a ________________ coloration. It usually eats __________________, but if it eats other microbes it becomes a giant Blepharisma. The giant Blepharisma becomes a _______________________ and eats its own kind. It is covered with tiny __________________ called ________________. The cilia are used like paddles for swimming or to push food in its mouth. To reproduce, the Blepharisma ________________ itself in half to produce twins. This is called ___________________ ______________________ Draw a diagram of binary fission (when the nucleus splits in half to reproduce) Vinegar Eels The vinegar eel is a harmless _______________ _______________. It is about __________ long. Its body is almost _________________ and you can see some of their organs. Vinegar eels are made of many _________________. It is one of the lowest animal forms that can ________________ ____________. It has a ________________ and an __________________. Females have their ___________________ lined up inside of them by ___________. Vinegar eels are only found in ________________________ vinegar. Pasteurization is a process where a ______________ is heated to a very high _________________. This sterilizes the vinegar, which kills all the ____________________ Identify the cell terms _________________: the thick covering of a plant cell made from _________________ fibers __________________: a thin, _________________ cell covering (lets gases in and out) _________________: the cell part that _______________ activities of other cell parts (the brain of the cell) __________________: storage ________________ in a cell (stores water and waste) _________________: the ___________________ fluid between the cell membrane and the nucleus. (jello) ______________________: the _______________ cell part that traps sunlight. (jellybeans) ___________________: the powerhouse of the cell that releases _________________________. All living things are made up of _____________________ Draw and label a plant cell Draw and label an animal cell How are plant and animal cells different. 1. 2. ___________________ ___________________ ___________________