* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download genetics review sheet
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
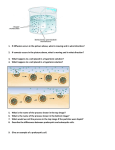
GENETICS REVIEW SHEET QUESTION 1. What is meiosis? 2. What are gametes? 3. How many cell divisions are there in meiosis? 4. How many sperm are made in meiosis? 5. How many eggs are made in meiosis? 6. How many chromosomes do your body cells have? 7. How many chromosomes do your sex cells have? 8. If a moth has 20 chromosomes in its body cells, how many are in its sex cells? 9. What is Klinefelter Syndrome? 10. What is Down Syndrome? 11. What is Turner Syndrome? 12. On what chromosome number can you determine the sex? 13. What is a karyotype? 14. What chromosomes make you a boy? 15. What chromosomes make you a girl? 16. How many strands make up DNA? 17. How many strands make up RNA? 18. What are the building blocks of DNA? 19. What is this building block made of? 20. If 40% of a DNA strand is make of A’s, what percentage is made of G’s? 21. The A base always compliments which base? 22. The C base always compliments which base? 23. What are the 4 nitrogen bases? 24. Complete the complimentary DNA strand: ACTCTGGCTTAACGTTAAGTACGATCGGA 25. Complete the mRNA strand and protein sentence: TACTCTAAAGGGACGATTCGTACTTGA ANSWER mRNA protein 26. Restriction Enzyme BB reads GGCCTT and cuts between the G’s: ATCGGCCTTGCTTATCGGCCTTAAGCTTGGCCTT a. How many fragments are there? b. How many bases are there in each fragment? 27. What are the two steps in protein synthesis? 28. Where does the first step occur? 29. Where does the second step occur? 30. What happens in the first step? 31. What happens in the second step? Punnett Square Practice A group of students wanted to determine how the ability to taste PTC, a nontoxic chemical, is passed from one generation to the next. The students decided to test families in their community for this ability. The students gave each family member a paper strip coated with a small amount of PTC. Those who experienced the bitter taste of PTC when they touched the paper strips to their tongues were called "tasters"; those who could not taste the PTC were called "nontasters." The results of the experiment are shown in the table below. 1. Explain how two taster parents could produce a nontaster child? 2. Based on the data the students collected, the allele for tasting PTC is most likely a. Dominant b. Heterozygous c. Recessive d. sex-linked 3. In humans, the allele for dimples (D) is dominant. The allele for not having dimples (d) is recessive. A woman (DD) and a man (Dd) have four children. What is the predicted ratio of the children with dimples to the children without dimples? 4. In humans, the trait for having a second toe that is longer than the big toe (T) is dominant; the trait for having a second toe that is shorter than the big toe (t) is recessive. The two traits are shown in the figure. A family has eight children. Six children have second toes that are longer than the big toe. Two children have second toes that are shorter than the big toe. What are the most likely genotypes of the parents? 5. The allele for attached earlobes (e) is recessive to the allele for unattached earlobes (E). A woman with the genotype (Ee) and a man with the genotype (ee) have a child. What is the probability that the child is heterozygous for attached earlobes? 6. In a species of fly, the allele for red eyes (R) is dominant to the allele for brown eyes (r). Students crossed male and female flies that had red eyes and recorded the eye color of their offspring. Their data are as shown below. What are the most likely genotypes of the parent flies? 7. Hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells, carries oxygen. Abnormal hemoglobin cannot carry as much oxygen as normal hemoglobin. The sequences below show section of the DNA sequence that produce both the normal and abnormal type of hemoglobin. Normal DNA Sequences: Abnormal DNA Sequences: SECTION OF GENE FOR HEMOGLOBIN GGA CTC CTC GGA CAC CTC MESSENGER RNA CODON TABLE CODON GUG CAC CUC ACU CCU GAG AMINO ACID Valine Histidine Leucine Threonine Proline Glutamic Acid Answer the following questions on your paper: a. Write the Messenger RNA (mRNA) sequences that would be produced from the normal and abnormal DNA sequences shown above. b. Using the codon table, write the amino acid sequences produced for the normal and abnormal hemoglobin. c. Beginning with DNA, describe the process that form proteins such as hemoglobin. (HINT: Protein Synthesis)