* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - Net Start Class
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
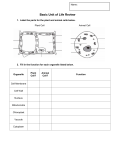
Name: Class Period: Week 18 CCA Study Guide Remember this worksheet is meant only to be a guide to help you prepare for the up coming test. You should also access the online textbook, study your journal, and cell diagrams. TROPISM Hydrotropism Geotropism / Gravitropism Phototropism Thigmotropism ORGANELLE Many Small Vacuoles One Large Vacuole Cell Wall Cell Membrane Chromosomes / DNA Nucleus Ribosomes Mitochondria Chloroplast / Chlorophyll Endoplasmic Reticulum STIMULI Moisture Gravity Dim/Bright Light Fence post, tree, side of a house PLANT CELL X X X X X X X X X RESPONSE Roots grow toward water Roots grow down, stems up Plants bend toward light Plant “climbs” up object ANIMAL CELL X X X X X X X 1. Why do we refer to the nucleus as the “brain” of the cell? The nucleus contols all the activities of the cell like the brain controls the activities of the body 2. Which organelle is called the cell’s powerhouse AND why? The mitochonria is called the powerhouse because it “digests” glucose to release energy for the cell to use. 3. What are the 3 main parts of The Cell Theory? 1) all living things are made of cells 2) all cells come form pre-existing cells, and 3) the cell is the basic complete unit of living things. 4. Describe the process of photosynthesis – include the organelle where it takes place, the reactants (what it needs), the products (what it produces), and the energy transformation that takes place. During photosynthesis plants use water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen. The process takes place in the chloroplasts of green plant cells and transforms radiant energy (sunlight) into chemical energy (glucose) 5. What could a person observe at the cell level and organism level that would indicate that a plant was suffering from dehydration? At the cell level using a microscope a person may observe the cell membrane pulling away from the cell wall and the vacuole shrinking. At the organism level a person would observe wilting – drooping branches and leaves. 6. What is Turgor Pressure and why is it important? Turgor Pressure is the pressure exerted by water pushing on the sides of the cell vacuole. Plants do not have skeletons so Turgor Pressure helps keep the plant up right. Having a full vacuole also insures a water supply for photosynthesis and other chemical reaction taking place in the cell. 7. List the levels of organization in the body from smallest to largest. Cells >>>> Tissues >>>> Organs >>>> Organ Systems >>>> Organism Complete the Chart Below STRUCTURE Nucleus Vacuole Lysosome Cell Wall Mitochondria Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Chloroplast Cytoplasm Cell Membrane FUNCTION Control the activities of the cell Store water, food, some waste Breakdown molecules, waste Rigid, give support and shape Produces energy for the cell Synthesizes proteins Assembles molecules and transport them across the cell Transform radiant energy into chemical energy (glucose) Jellylike substance keeps cell organelles in place Surrounds the cells controls what enters and leaves the cell BODY SYS or Organ Brain, Nervous System Urinary bladder, large intestine Liver, digestive system Skeletal System Digestive system, adrenaline Muscles Circulatory System (blood vessels) Digestive system, Skin/Integumentary System (production of vitamin D) Connective tissue (tendons, ligaments, mesentery) Alveoli, Digestive System Skin, Integumentary System 8. How might your body respond if you had an infection such as strep throat? Your throat may become red, inflamed, and sore. White blood cell count may increase, you may develop a fever 9. When your body is preparing to “fight or flight” what changes might you experience? Adrenaline is released by the adrenal glands. Increased heart rate, respiration rate, and blood pressure. Your senses become more acute (very alert) and your muscles taunt. 10. Indicate if the following are examples of Internal (I) or External (E) stimuli. feeling hungry I feeling heat from a flame E stepping on a rock E low blood sugar levels I low blood oxygen levels I fire alarm E you salivate when you smell cookies cooking E tickle in your throat I lack of food E lack of water E 11. Indicate if the following are examples of stimuli (S) or a response (R). sweating R increased blood pressure R increase insulin levels R plant wilting R 12. shivering R feeling thirsty goose bumps gravity S S R What force do your veins have to overcome to push your blood back to your heart? Veins have to exert a force strong enough to overcome the force of gravity