* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell In Its Environment Slide Show Notes
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
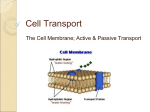
THE CELL IN ITS ENVIRONMENT POWER POINT NOTES Key Terms • Some substances can pass through the membrane while others cannot. • In diffusion, molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. • The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane is osmosis. • The movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane without using cellular energy is passive transport. • The movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy is called active transport. Introduction • Cells have structures that protect their contents from the world outside. • All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment. • The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which lets some things enter and leave the cell. • Name 3 substances that enter and exit a cell through either passive or active transport. oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, sugar, salt, potassium, waste materials, food particles What is Diffusion? • The process by which molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. • The main method by which small molecules move across the cell membrane. What is Osmosis? • The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. • Many cellular processes depend on osmosis because cells cannot function properly without adequate water. How is Osmosis related to Diffusion? • Water molecules move by diffusion from an area where they are highly concentrated through the cell membrane to an area where they are less concentrated. Effects of Osmosis on Cells • Cells placed in distilled water will swell and can possibly burst. • Cells placed in a concentrated salt solution will shrink and shrivel. What is Passive Transport? • The movement of materials through a cell membrane without using energy. • Diffusion and osmosis are examples of passive transport. What is Active Transport? • The movement of materials through a cell membrane using the cell’s energy. • Give two reasons why active transport may occur instead of passive transport (diffusion/osmosis). substance are too large to fit naturally through the cell membrane substances are going against the concentration gradient Methods Active Transport • List 3 ways a cell uses active transport to move molecules/substances between the cell and its environment. transport proteins “pick up” engulfing “Transport” is like Riding a Bike? Passive Transport is like riding a bike down a hill. Active transport is like riding a bike up a hill. Why are Cells Small? • The smaller they are the easier it is for them to do their job.