* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (key)
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry 256
Sample mid-quarter exam 1 (winter 2015)
1.
Which one of the following processes is not stimulated by insulin?
a. Glucose uptake in muscle (t-j1.7f '-''";r·)
b. Dephosphorylation of glycogen synthase in muscle -'lc.h\kAt,.s ~JtJI'YtY
c. Glycolysis in the liver
d. Dephosphorylation of glycogen synthase in liver
G;>Ail of the processes listed are stimulated by insulin
2. a Which enzyme would you use to remove a phosphate group from the enzyme
glycogen phosphorylase a to form glycogen phosphorylase b
Phosphorylase kinase
Protein kinase
()>hosphoprotein phosphatase
Glucose Phosphorylase
b. Would this event activate o~r have no effect on the enzyme glycogen
phosphorylase?
c. The above event is considered a (circle all that apply):
~t modification of an enzyme
Allosteric modification of an enzyme
Genetic modification of the enzyme
~le of an enzymatic cascade
3· Cyclic AMP is considered a:
Hormone
Steroid
~ond messenger
A receptor
Enzyme
4. Chylomicrons contain which molecules:
Acety-CoA
~lesterol esters
Glycogen
Isoprene pyrophosphate
(J)iacylgly~rides
5· Circle which below would give a membrane a higher melting point
aCii7
@
@
Incorporation of more cholesterol
Longer Chain lengths of the fatty acid components
Less unsaturation of the fatty acid components
Cross linking of fatty acid components
6. For integral proteins associated with cell membranes what type of amino acid
residues would be found exclusively within the membrane.
l\)0'1\ -
r c)' (;\(""
7· While fatty acids are most often formed by the condensation of_-carbon units,
isoprenoids are assembled from _-carbon units.
a.5,3
b. 4, 2
c. 2, 3
(g) 2, 5
e. 3,4
8. Which enzyme catalyzes the key regulatory step of cholesterol synthesis?
a. b-ketothiolase
b. HMG-CoA synthase
(S:>HMG-CoA reductase
d. mevalonate kinase
e. squalene monooxygenase
9. In Gluconeogenesis the steps that are simply the reverse of Glycolysis
c;)) Have a ~G that is near o.
~
~ Have a ~G that is a large + value
c) Have a ~G that is a large- value
d) Are considered the rate control steps
e) All step are the reverse of glycolysis
10. If the liver is analyzed, and the ratio of phosphorylase a (active form) to
phosphorylase b is found what processes would probably be occurring?
Gluconeogenesis
Glycolysis
L:Blycogen breakdown
Glycogen build up (synthesis)
---~-----···-··-----
11. Which synthetic pathway(s)
does the class of drugs called 'statins' effect
Gluconeogenesis
Glycolysis,
Glycogen breakdown
Glycogen build up
(9holesterol synthesis
Fatty acid synthesis.
12.
Which pathways does Acetyl CoA participate in (as a reagent or product)?
Gluconeogenesis
Glycolysis
Glycogen breakdown
Glycogen build up
C;Xholesterol synthesis
~eta oxidation of fats
~itric acid cycle
Cfatty Acid synthesis
Terpenes
~-<o
Spingolipids~
9
~
<>-
f -0 oe>
0~
'
l,j.il.-Cti-Cpol
~"
\
o-:.C.
-tz..
I _,.. o /
4.1 ~ti -,.....
'!'.I.,. sa
t\$
u
14. Which molecules drawn above would you attribute the property of amphipathic. """'~'l"r',.c.P'\' :s
Sf" I "''i() I, f'i!lS
15. Which processes below consume more energy than they produce? (consume ATP,
NADPHetc)
Cf;.Iuconeogenesis
Glycolysis
Citric acid cycle
~holesterol synthesis
Pentose-f)hosphats-pathway- JJ~ ~ '4A~
Fatty acid oxidation
~tty acid biosynthesis
16. What make the isopentyl pyrophosphate molecule so reactive? -
1
r
'\ofi·As
s
fa~lL.- at"b~tt-hCI\tl
r.UDflll"'tt
.\.
1
I
SrAQI 111'
17. DescribetheroleandpurposeofProstaglandins lDc~\ ll.ejk\"~"n
~louet
1 fo.in, bloool Ctotl'Y'cJ
P'\.l.Jsl4.1\.t.l
\==ever
~~~~~~~le has a higher energy density by weight-Glycogen or
ffn5
19. In the synthesis of glycogen, pyrophosphate (PPi) is hydrolyzed by water to form 2
phosphate groups. What is the purpose of this step? Is what other synthesis does this
occur?
-ro (;~-T.t.- ~5( ~ W\o\..{_ -l\,..tjl.tD--t+,41 .fovwa~~"~.
f-r, .or ~t-o~ L.; Pt -r e'"""S!
CO!AflRcl_ to enclO')Jo"r\lL f"£c.Ltn.~
20
B What enzyme was used for this step
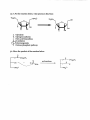
21. A For the
reaction below, what process is this from:
a. Glycolysis
b. Cholesterol synthesis
c. Fatty acid biosynthesis
B-o:xidation
e. Gluconeogenesis
f. Pentose phosphate pathway
6!;>
0
SCoA
SCoA
22B What enzyme was used for this step?
a. Phophofructokinase
b. Lipolphosphatase
c. AcetylCoA-Carboxylase
d. Hydroxyl acetyl dehydrogenase
[?Enoyl-coA hydratase - Ad~ I n3' HVJ
23 For the reaction below, draw in the arrow pushing mechanism of the next step .
where 2,3 oxidosqualene is converted to the basic cholesterol structure
NADPH
NADP+
\...._/
squalene
epoxidase
Squalene
~:
2,3-0xldosqualene
0 200e John Wla., 6 Son-, Inc. AU rlghU rearved.
mechanism
Using the chart below answer 29-32
24. Which direction is glycolysis (goin~ or up)
25. Which direction creates energy (rather than consumes)? Doi...\N).
26. Which step is the allosteric inhibitor F2,6P important. 27, Which enzyme does F2,6P inhibit?
s v-el
fVLAttou. I;., ~pl,p!ph 11 ~s:.t.-
1
Qt,tol~s, s
st~
F" P _, r I hBf>
ncreased Glucagon secretion will promote which direction of this process
own) - - G\ t....t..CJh.t o~s·,s
Glucose
glucos:~:;;:
phosphatase
}:x::nase
H20
ADP
Glucose-6-phosphate
~ phosphoglucose isomerase
1
fructoS:~~~uctos...a-ph"'f::__-
phosphatase
H20
ADP
FructoM-1,6-blsphosphate
n•ldolase
triose phosphate
Dlhydroxyacetone Isomerase , Glyceraldehyde-3phosphate
phosphate
Pi+
NAD+~~NAD+
+Pi
glyceraldehyde-3-phos-
NADH + H+
phate dehydrogenase
NADH + H+
1,3-~sp~o h~ycerate
ADP
~ADP
phosphoglycerate
kinase
ATP
ATP
3-PhosphOglycerate
1~ phosphoglycerat~ mutase
2-Phosphoglycerate
n•nolase
CO,+GDP~
!i::oacetate
Pi+ADP
pyruvate
carboxylase
'v;~~:te
~ ATP
kinase
PJI'UVate
ATP+C02
o 2008 John Wiley & Sons. Inc. All rights reserved.
29. A For the reaction below, what process is this from:
OH
a.
b.
c.
d
Glycolysis
Glycogen synthesis
Fatty acid biosynthiss
B-oxidation
~luconeogenesis
f. Pentose phosphate pathway
30. Show the product of the reaction below:
o-c.;
R
OH
~
0
+
R~
~'
acy }transferase
SCoA
E
(tiT))~rl>
o-c.-TL
Df'O 2--
i