* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Stereopsis recovery wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Computer vision wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Bicameralism (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Visual extinction wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
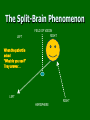
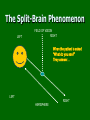
Biological Psychology – Module 4 The Split-Brain Phenomenon Synaptic Plasticity Intro Psych Feb 12-19, 2010 Classes #11-13 The Split-Brain Phenomenon Corpus Callosum The two sides of our brains serve different functions (lateralized or specialization of tasks): Large band of neural fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres Left hemisphere: Language, math, logic Right hemisphere: spatial abilities, face recognition, visual imagery, musical and artistic abilities, emotional tasks. This is the case for almost all righthanders (about 95%) and about half of lefthanders Important aspects of this divided brain phenomenon Information from left half of field of vision is received only by your right hemisphere, and information from the right half of your field of vision is received only by your left hemisphere Don’t get confused here as each eye receives sensory information from both right and left visual fields. But this information is only transmitted from a particular visual field to a particular brain hemisphere Important aspects of this divided brain phenomenon The left hemisphere receives information from and controls movements of the right side of the body, whereas the right hemisphere receives input from and controls movements of the left side of the body Tests show that almost all right-handers (over 95%) process speech in the left hemisphere Important aspects of this divided brain phenomenon Left-handers are more diverse: 60% process speech in the left hemisphere 5% process speech in the right hemisphere 35% use both hemispheres about equally (half of the time) Split-Brain Experiments Vogel and Bogen (1961) Sperry and Gazzaniga Conducted many experiments from 1960’s through the 1980’s The Split-Brain Phenomenon LEFT FIELD OF VISION RIGHT When the patient is asked “What do you see?” They answer… LEFT HEMISPHERE RIGHT The Split-Brain Phenomenon LEFT FIELD OF VISION RIGHT When the patient is asked “What do you see?” They answer… LEFT HEMISPHERE RIGHT The Split-Brain Phenomenon RIGHT LEF T FIELD OF VISION The same patient who has just said they could not see the picture is now asked to take their left hand and touch the ‘happy face” picture… What happens now??? LEF T HEMISPHERE RIGHT The Split-Brain Phenomenon RIGHT LEF T FIELD OF VISION Now, with the object in the patient’s hand, he/she is asked “what is in your hand”…what is their answer this time??? LEF T HEMISPHERE RIGHT Severed Corpus Collusom: Video 1st scene: “Joe” is flashed words in his right field of vision (“storm” and “piano”) and has no trouble saying them He is then flashed the word “phone” in the left field of vision…and he can’t say it “didn’t see that” But when asked to draw a picture of what he saw with his left hand…he draws a telephone but since its still in his left field of vision he still can’t verbalize what he just drew Severed Corpus Callosum: Video But then when asked to draw it with his left hand but in his right field of vision…he is able to say what he drew (“oh, phone”) Very interesting… Severed Corpus Collusom: Video 2nd scene: Joe is flashed words simultaneously in both fields of vision – “toad” in left field and “stool” in right field… He can’t say “toad” but can draw it with left hand He can say ‘stool” and by speaking it, he is able to let the right hemisphere in on the “secret” Severed Corpus Collusom: Video 3rd scene: Again, two words simultaneously…”bell” appears in his left field of vision and “music” in his right field of vision When asked to point with his left hand to what he saw, Joe points to a picture of a bell but is not really sure why so he makes up a story that seems to be plausible…he’s basically trying to figure out what's going on Severed Corpus Callosum : Video Joe’s left hemisphere is trying to interpret what is going on – trying to find a cause and effect Left hemisphere is responsible for making sense out of the mystery According to Gazzaniga: “the left hemisphere is where the action is”… Severed Corpus Callosum : Video Final scene: Pictures are shown of faces made out of fruit, meat, etc. Right hemisphere specializes in locating faces and left is better at finding elements involved… So what happens? Right hemisphere sees it as a face and left hemisphere sees it as a fruit Still being performed but now very rare Cutting apart the two hemispheres of the human brain is a drastic step, and it is one of the most controversial operations ever performed Yet it can succeed, when all else fails, in relieving violent, drug-resistant epileptic seizures This surgery is becoming more and more rare – Instead, neurosurgeons are using a variety of neuroscience techniques to reduce the amount of tissue removed in brain surgery Hardly ever performed now because also because of new and effective medications that help prevent seizures Brain Reorganization: Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic Plasticity Often when one area of the brain is damaged, other areas may in time reorganize and take over its function It is not uncommon for stroke patients who have lost the ability to speak or to move a limb to regain function after several weeks of convalescence How does the brain recover? Essentially what is occurring is a “remodeling” of the cerebral cortex after an injury in which sometimes a large part of it simply dies Of course, this is the exception and not the rule Not all stroke victims recover Even better chances: Plasticity in children Before the functions of young children’s cortical regions become fixed, their brains are especially plastic…if the speech areas of an infant’s left hemisphere are damaged, the right hemisphere will usually take over with no noticeable impairment of language… Left hemisphere damage does not permanently disrupt language until age 8 Case study: see hand-out Illustrates that the brain has extraordinary powers of reorganization, especially when damaged before it is fully developed